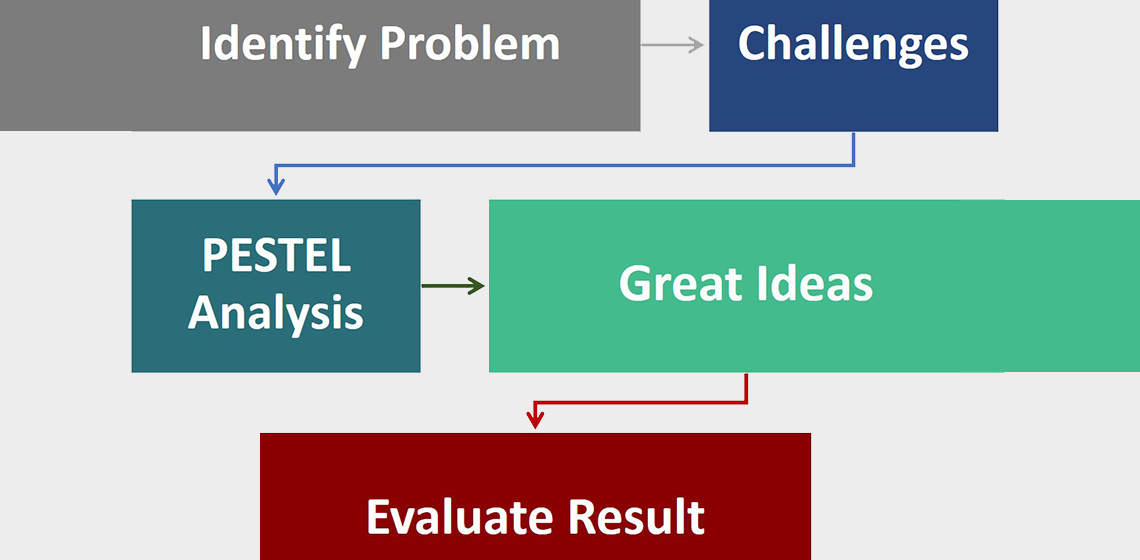
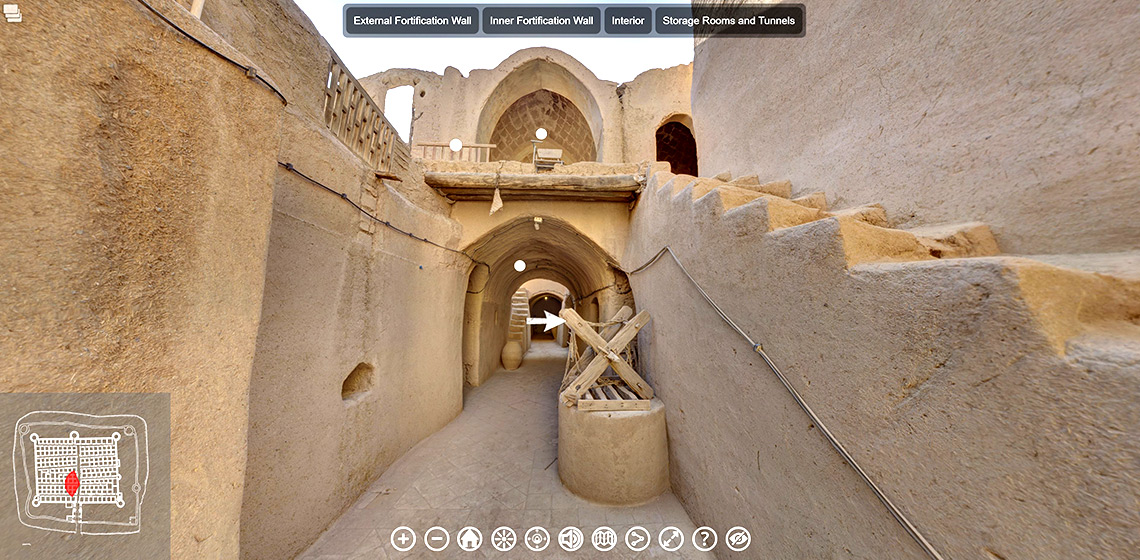
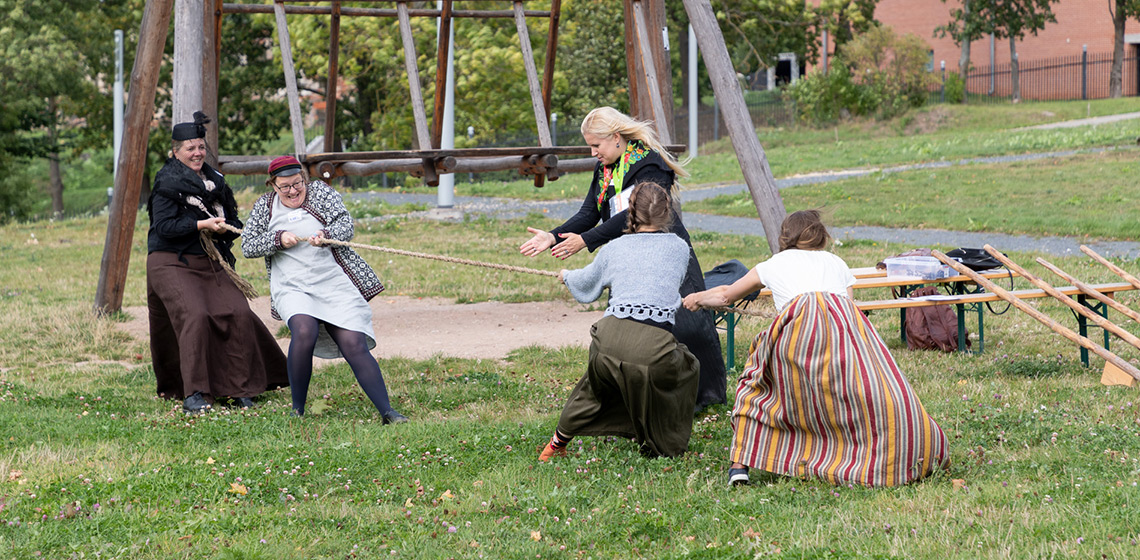Interpretation
Strategy of Presenting Prehistoric Sites Like an Open-air Stand. Why and How and from a Sustainable Development Perspective
Introduction
One of the heritage resources of prehistoric sites, where prehistory is a diverse and wide-ranging field of study, appears as the triple determination between geography and climate, humans and their type of social organisation. Prehistory has bequeathed us evocative monuments and landscapes from the earliest human occupation, spanning enormous environmental and technological changes, and including several human species. Thus, prehistoric sites have great meaning in both natural and cultural history.
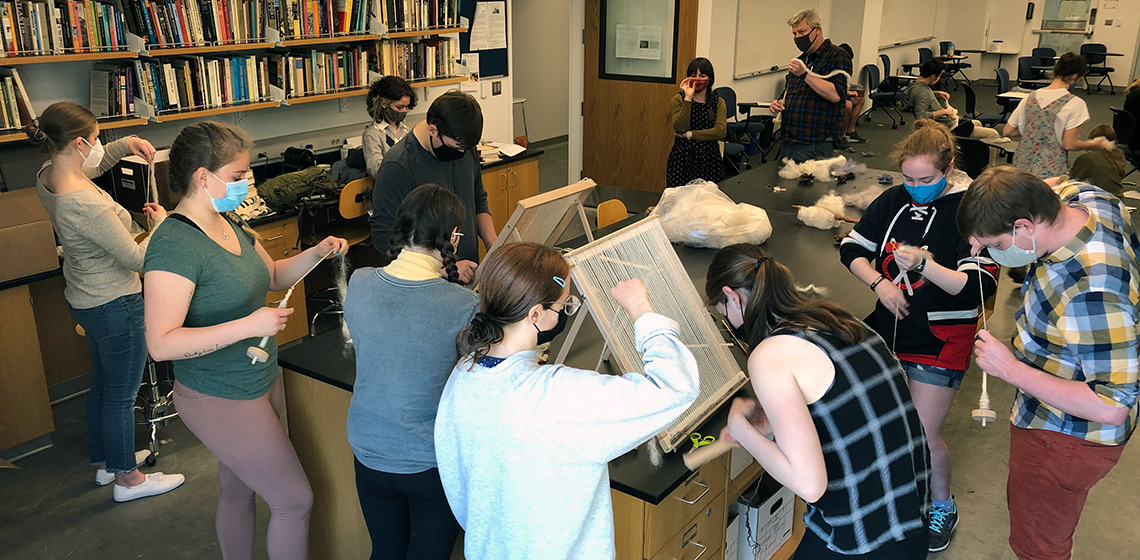
Launching an Experimental Archaeology Course at the Undergraduate Level
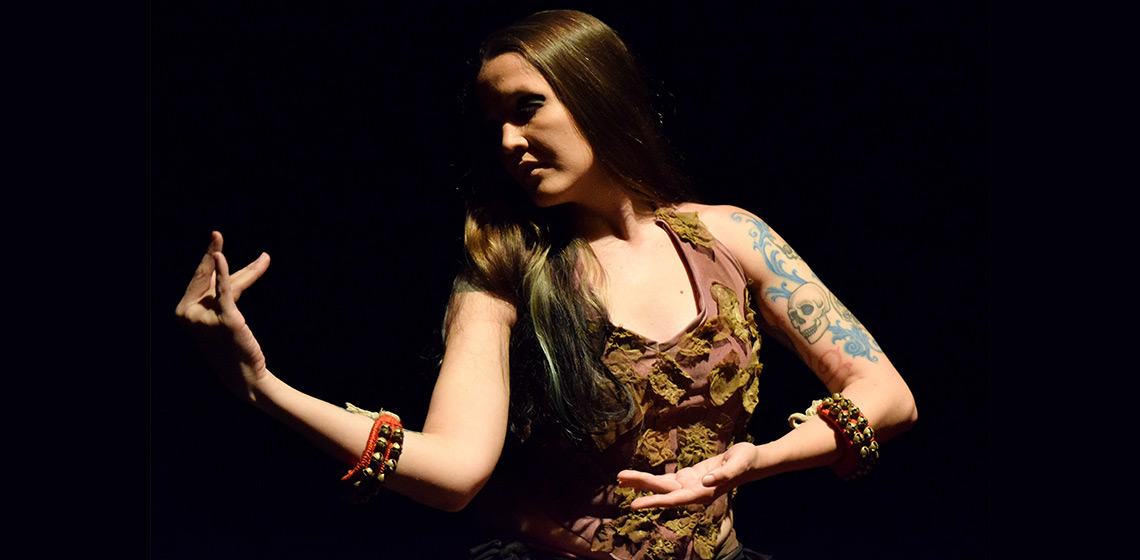
The Experimenter's Body: Movement as an Artifact
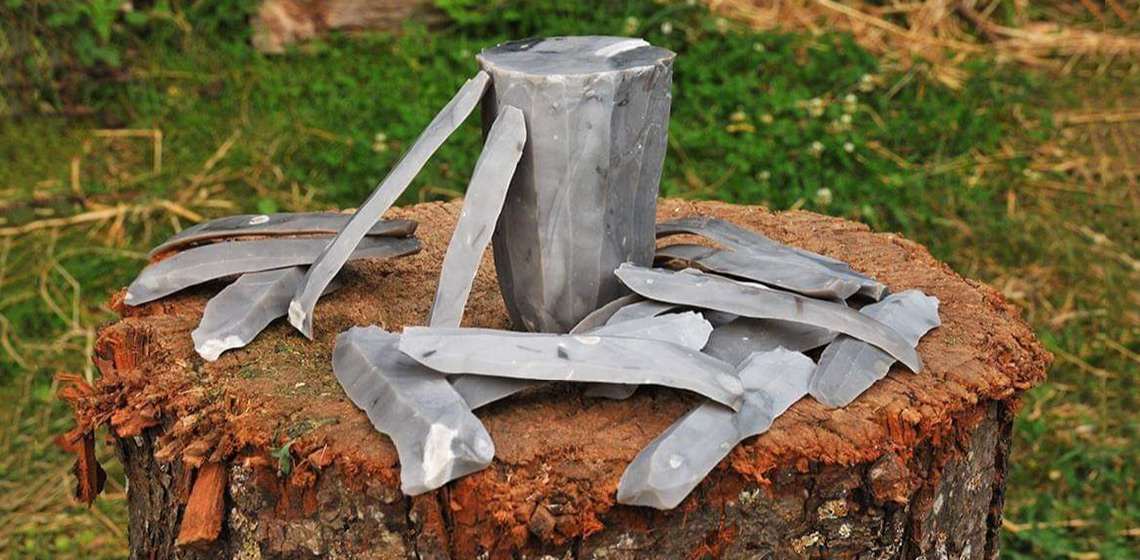
Let the Chips Fall Where They May: Evaluating the Impact and Effectiveness of Video Resources for Knowledge Transfer in Flint Knapping
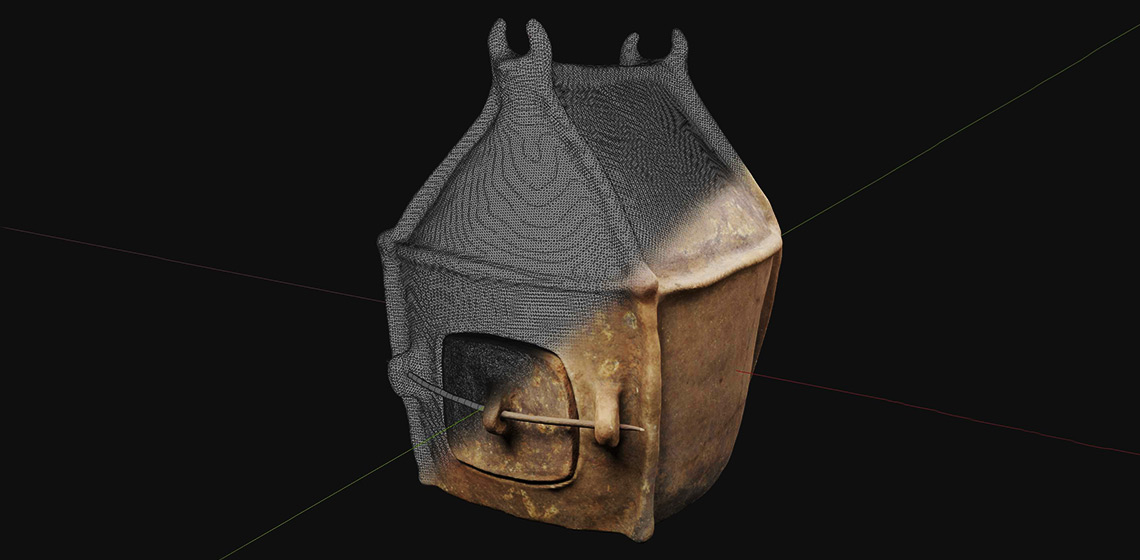
Blending the Material and the Digital: A Project at the Intersection of Museum Interpretation, Academic Research, and Experimental Archaeology
The Development of the 1st Cultural Exchange of Traditional Knowledge and Experimental Practices of the Peruaçu River Basin
Introduction
The Peruaçu National Park is a nature conservation unit located in the environs of the Peruaçu River basin, in the North of the State of Minas Gerais, and it preserves an area for the Cerrado biome of Brazil. The Cerrado is an area of 2 million square kilometres and is the second largest biome covering the Brazilian territory. However, just 20% of it is preserved. The region of the Peruaçu National Park belongs to this preserved 20%. On it is one of the most important archaeological sites of rock paintings in the state of Minas Gerais.
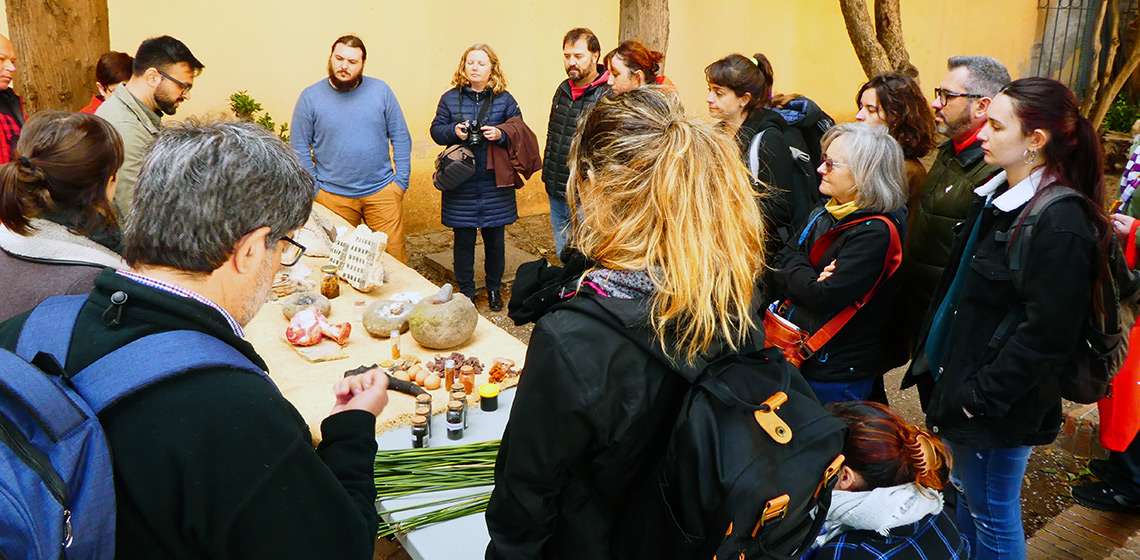
Experimental Archaeology in the Museum of Archaeology of Catalonia
***The Museu d'Arqueologia de Catalunya (MAC) was created under the Museums of Catalonia Act in 1990 by the Department of Culture of the Government of Catalonia. Its foundation dates back to 1932. The museum carries out various activities related to Experimental Archaeology projects in the fields of both education and research...