post depositional process
Trampling Experiments – A Contribution to the Pseudo-Retouch Issue
Publication Date
11th EAC Trento 2019
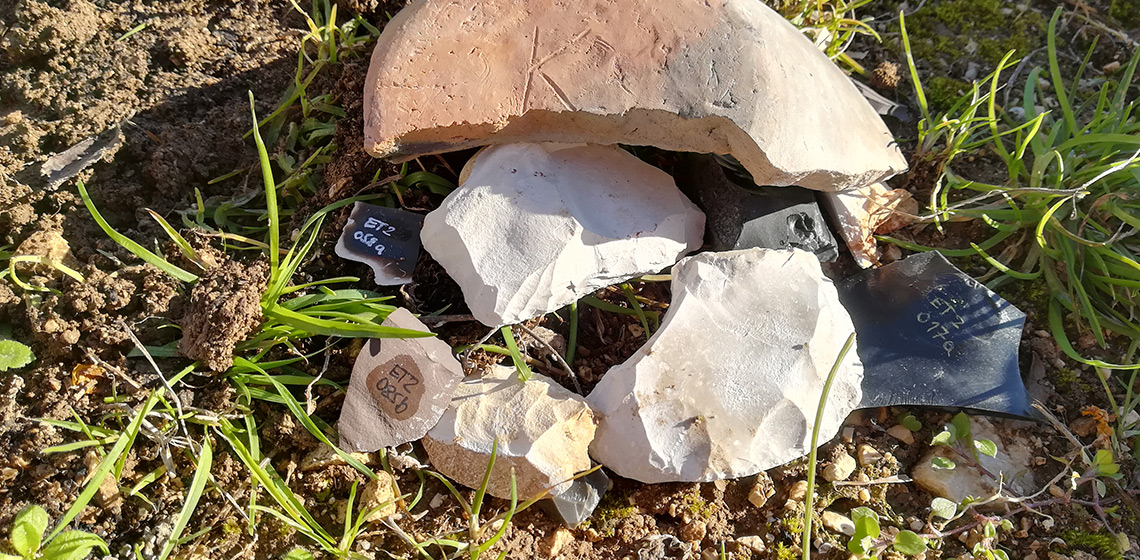
***Apart from human-made retouch, stone tools can also exhibit traces of damage caused by several post depositional processes, one of which is trampling. Edge damage provoked by trampling, be it of animal or human origin, is sometimes interpreted as human-made retouch ...
***Apart from human-made retouch, stone tools can also exhibit traces of damage caused by several post depositional processes, one of which is trampling. Edge damage provoked by trampling, be it of animal or human origin, is sometimes interpreted as human-made retouch ...
Comparing Mummification Processes: Egyptian & Inca
Publication Date
This two-year research project was carried out as part of SUNY Potsdam’s Presidential Scholars program which allows undergraduates to conduct independent research. The project employs controlled laboratory experiments to compare desiccation rates in natural and artificial mummification processes while considering the cultural context of the funerary practices. Artificial mummification techniques of ...
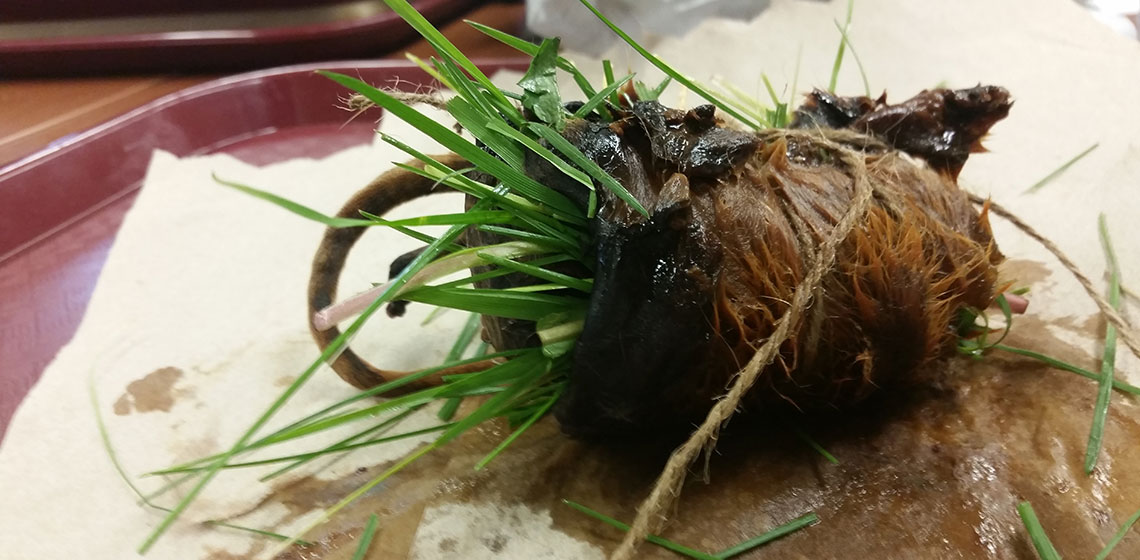
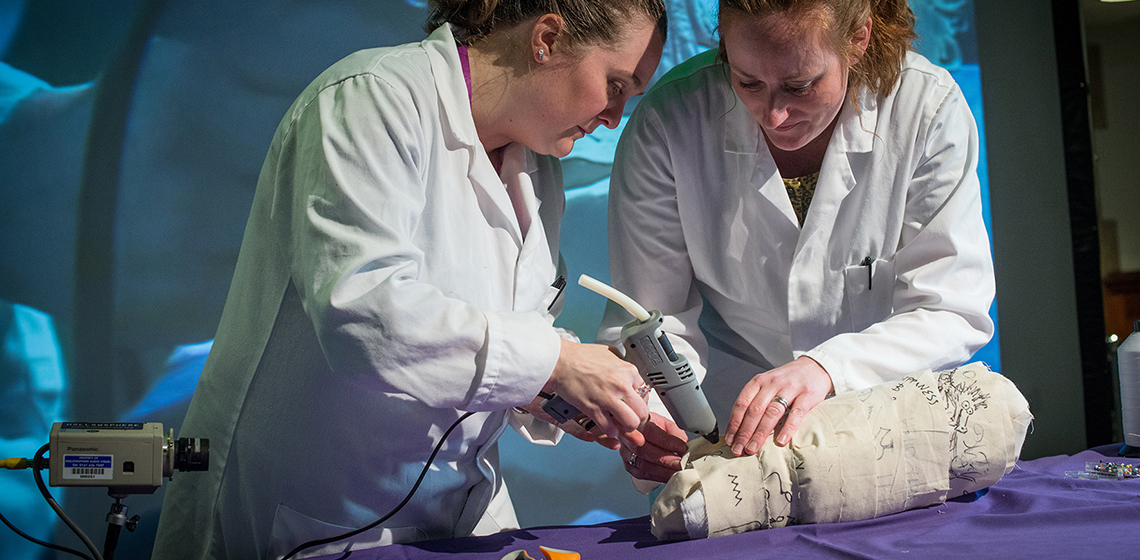
‘Re-rolling’ a Mummy: an Experimental Spectacle at Manchester Museum
Publication Date
10th EAC Leiden 2017
***Ancient Egyptian animal mummies and votive statuettes were often wrapped in linen, concealing the contents and conferring sanctity to the remains. Mummy autopsies were commonplace in 19th century Europe, when ancient mummified bodies were unwrapped to reveal what lay beneath the linen bandages. Similarly, votive statuettes were often unwrapped upon discovery, either by...
***Ancient Egyptian animal mummies and votive statuettes were often wrapped in linen, concealing the contents and conferring sanctity to the remains. Mummy autopsies were commonplace in 19th century Europe, when ancient mummified bodies were unwrapped to reveal what lay beneath the linen bandages. Similarly, votive statuettes were often unwrapped upon discovery, either by...
Book Review: Forensic Archaeology: the Application of Comparative Excavation Methods and Recording Systems by Laura Evis
Publication Date
This book is a rewrite of Evis’ PhD thesis compiled between October 2010 and March 2014 at Bournemouth University (University of Exeter 2017). The study was an evaluation of the archaeological excavation methods and recording systems used in the United Kingdom, Ireland, Australasia and North America...
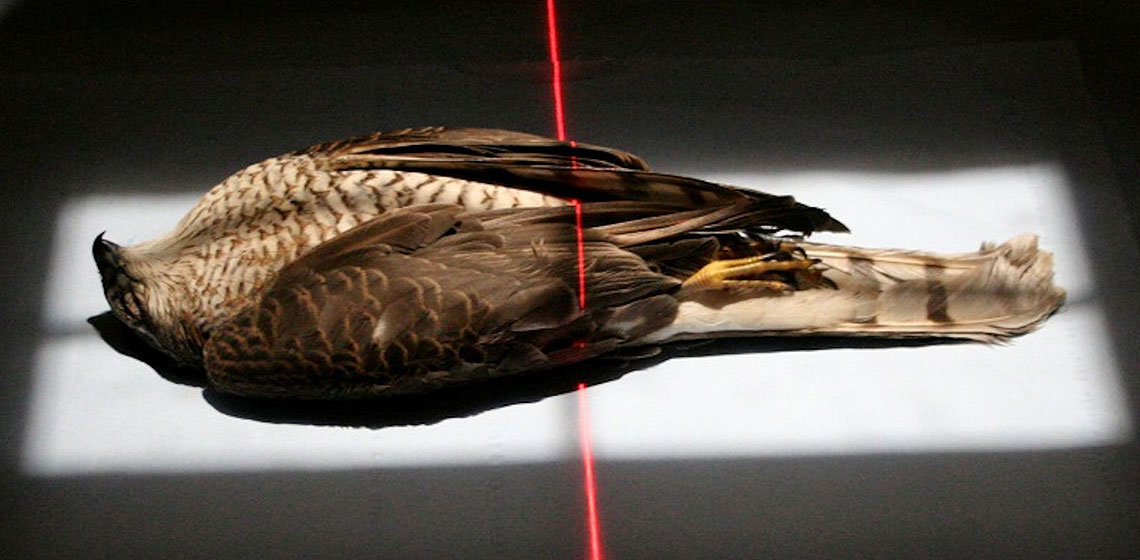
The Mummification of Votive Birds: Past and Present
Publication Date
7th UK EA Conference Cardiff 2013
***A mummy is defined as a ‘well-preserved dead body’ (Cockburn, Cockburn & Reyman 1998, 1), achieved by either natural or anthropogenic methods and refers to both human and animal subjects. Mummies achieved through both these methods are found in ancient Egypt as a result of preservation through desiccation, achieved by direct contact between the corpse and a dry, sandy matrix (natural); or through the use of natron (anthropogenic), coupled with evisceration (the removal of the internal organs) and anointment with resinous compounds, followed by wrapping the corpse in layers of linen (Ikram and Dodson 1998; Taylor 2001).
***A mummy is defined as a ‘well-preserved dead body’ (Cockburn, Cockburn & Reyman 1998, 1), achieved by either natural or anthropogenic methods and refers to both human and animal subjects. Mummies achieved through both these methods are found in ancient Egypt as a result of preservation through desiccation, achieved by direct contact between the corpse and a dry, sandy matrix (natural); or through the use of natron (anthropogenic), coupled with evisceration (the removal of the internal organs) and anointment with resinous compounds, followed by wrapping the corpse in layers of linen (Ikram and Dodson 1998; Taylor 2001).
Book Review: Experimental Archaeology and Fire. The Investigation of a Burnt Reconstruction at West Stow Anglo-Saxon Village by Jess Tipper
Publication Date
What should an archaeologist do if one of the reconstructions of an experimental village is accidentally burning during the night? Simple: pick up a camera and start taking pictures. And then, of course, plan the excavation to record as much information as possible followed by an analytical and detailed publication on the results...
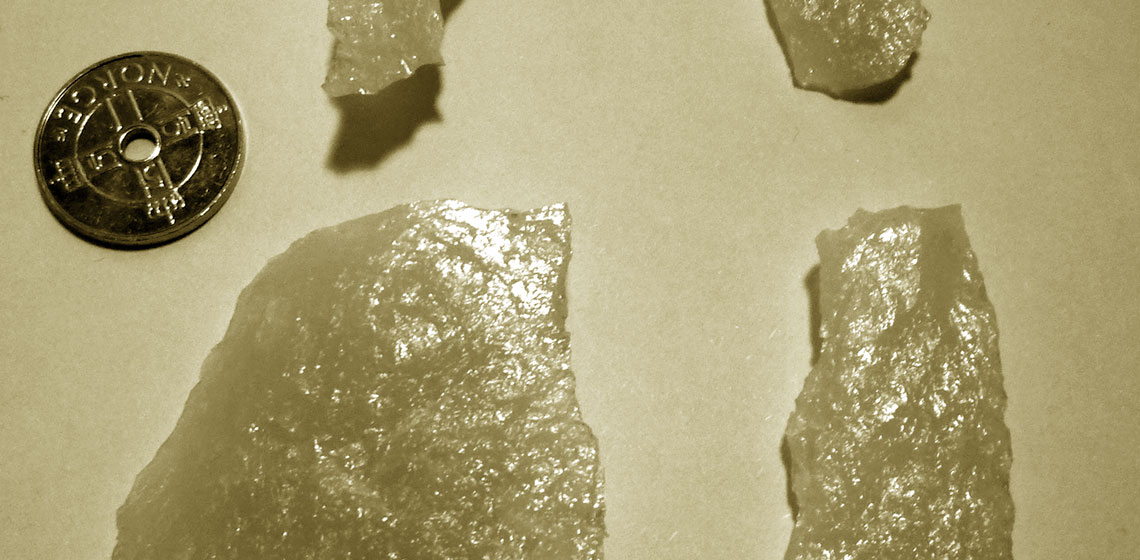
Lithic Experiments in Rescue Archaeology: a Case from Southern Norway
Publication Date
7th UK EA Conference Cardiff 2013
***The institutional context in which Stone Age knowledge production takes place in Norway is structured by the current system of cultural heritage management (CHM). By virtue of the Heritage Act from 1978 and the regulations on professional responsibilities, the practical work of surveying and excavating prehistoric sites is divided respectively between the 19 County Councils and the five archaeological government museums...
***The institutional context in which Stone Age knowledge production takes place in Norway is structured by the current system of cultural heritage management (CHM). By virtue of the Heritage Act from 1978 and the regulations on professional responsibilities, the practical work of surveying and excavating prehistoric sites is divided respectively between the 19 County Councils and the five archaeological government museums...