bone
“Look at the Bones!” - Adding Bone in a Bloomery Iron Smelt
Publication Date
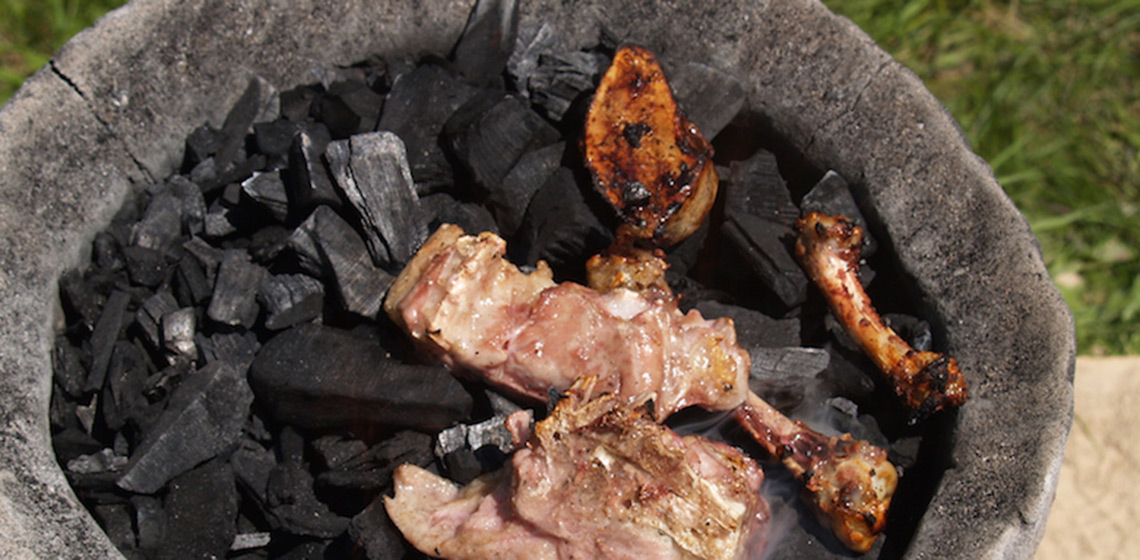
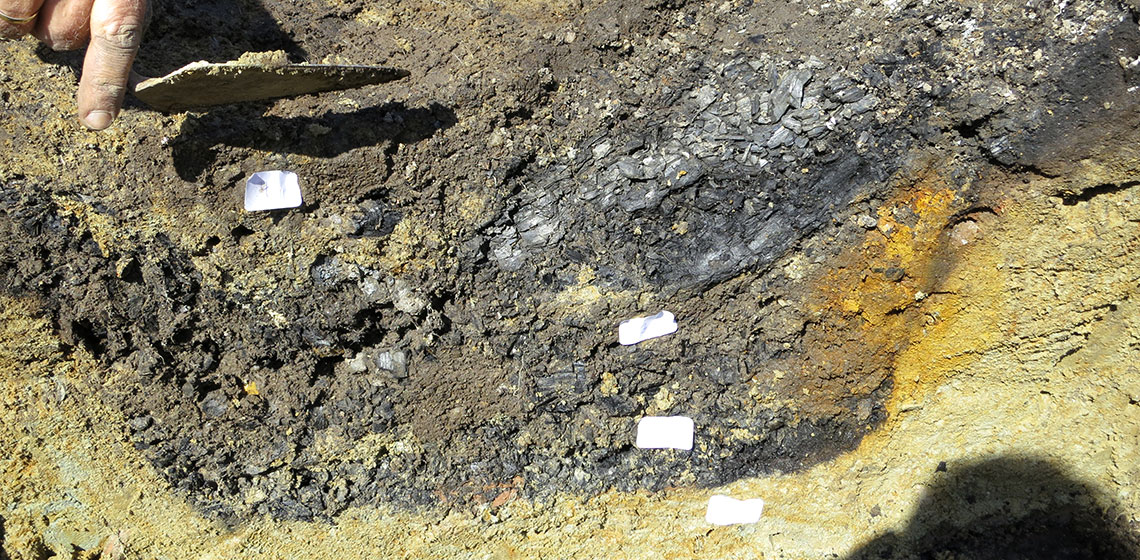
A case study of a practical experimental test. Through 2019, much was made in the popular press suggesting that during the Viking Age, exhumed human bone had been used in the chain of production from iron ore through to finished swords. Contradicting this, considerable experience with small scale direct reduction process bloomery iron smelting furnaces indicated...
Different Types of Needles for Specific Uses? Experimental Reproductions of some Finds from Aradetis Orgora, Georgia
Publication Date
This research aimed to evaluate some new hypotheses about the production and use of a class of pointed tools from the Bronze Age layers of Aradetis Orgora (Georgia), which have been traditionally considered as pins. Its main goal was to provide an alternative interpretation of their function, namely as tools used in basketry...
Roman Bone Artefacts – First Steps Towards a New Approach
Publication Date
To date, archaeologists often use a typological approach to assess the functions of bone artefacts from the Roman period. In some of these assigned typological groups, certain artefacts do not have a clear definition. This study aimed to assess whether use-wear analysis combined with experimental archaeology could be applied to bone artefacts from the Roman period as ...
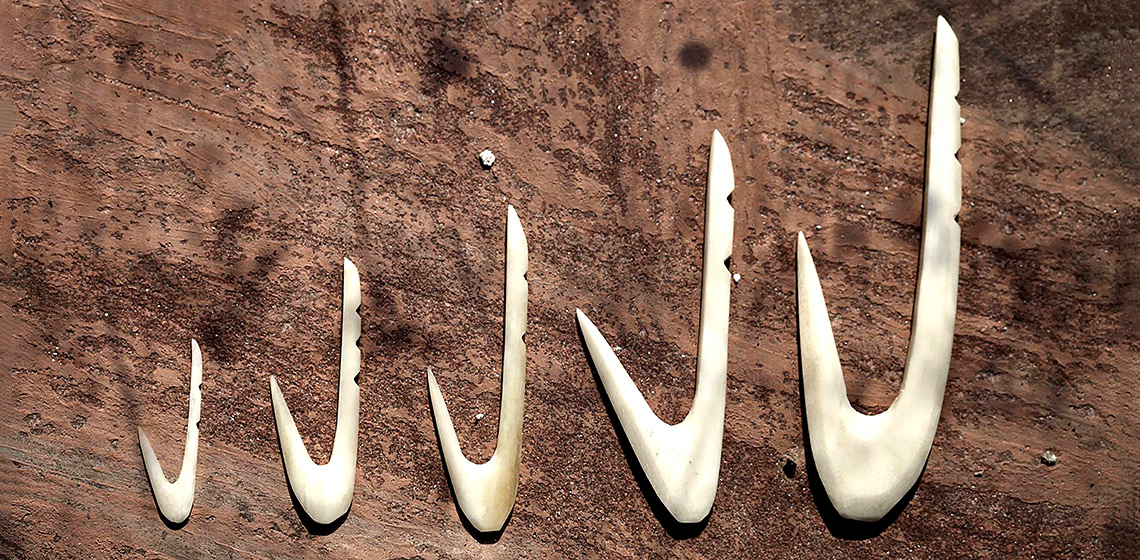
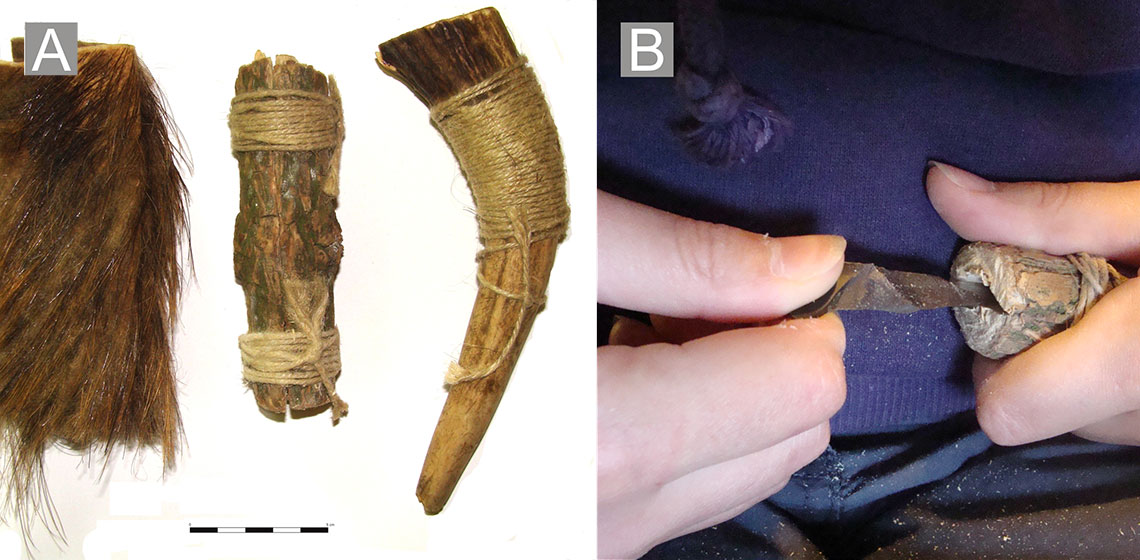
Roe Deer as Raw Material for Middle Mesolithic Fishhooks? An Experimental Approach to the Manufacture of Small Bone Fishhooks
Publication Date
Bone fishhooks have occasionally been retrieved from bone assemblages at coastal sites dating to the Middle Mesolithic phase (8300-6300 cal. BC) in Southern Norway and Western Sweden. Several studies of fishhooks from these sites have been undertaken in recent years. Fishhooks can be manufactured from different osseous materials, including antler, ribs and shafts of different long bones...
Spinning in Circles: the Production and Function of Upper Palaeolithic Rondelles
Publication Date
Rondelles are thin, circular disc cut-outs typically made from the blade of the scapula of medium sized ungulates, such as horse or cervid. These are primarily associated with the Late Upper Palaeolithic Magdalenian and focused around northwest Europe. Rondelles are frequently...
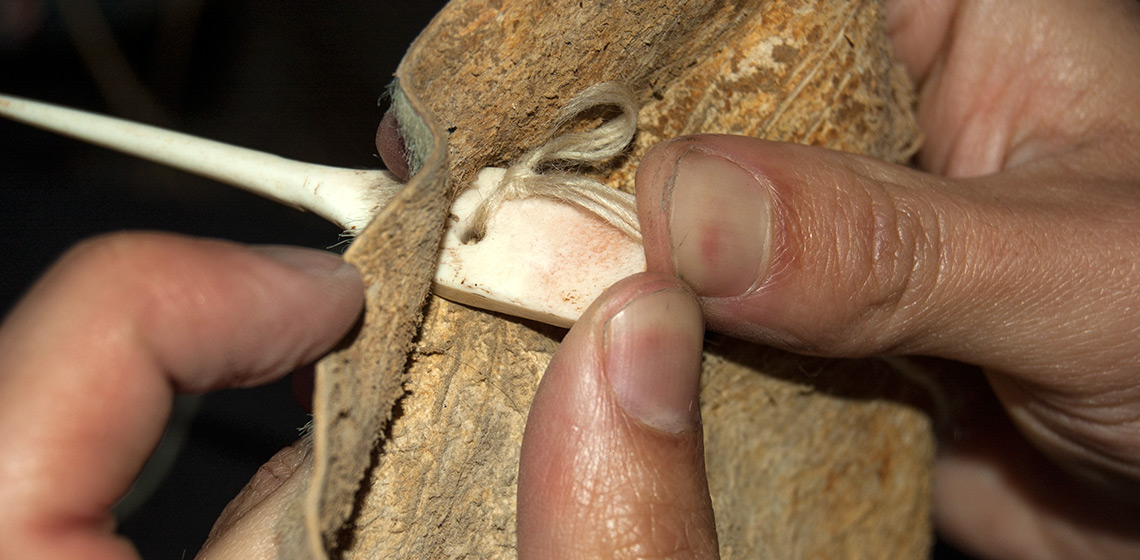
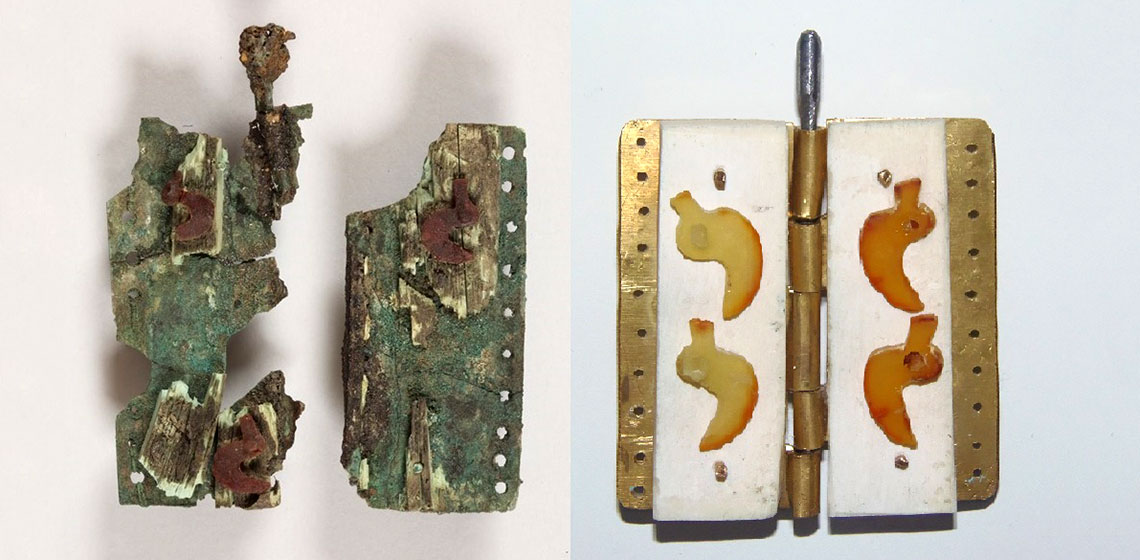
A Seventh Century BC Picenian Cloack Clasp Made of Iron, Bone, Bronze and Amber: Reconstruction of a Masterpiece
Publication Date
This article is dedicated to the reconstruction I’ve done in 2017 of a Picenian cloack clasp which is a pretty unique find. It has been found in a prince’s grave dating back to the early 7th Century b.C. and is considered a rare find because only a few similar items have been found in Central Italy, and because of the rare use of amber decorations and bronze plates, that makes this find a true masterpiece...
Twenty Years with Flint. The Society for Experimental Prehistoric Archaeology – Where are We Now?
Publication Date
The Society of Experimental Prehistoric Archaeology (SEPA, www.keap.umk.pl) is an organisation affiliated with the Nicolaus Copernicus University’s Institute of Archaeology since 1998. The first academic supervisor of SEPA was Jolanta Małecka-Kukawka, now led by Grzegorz Osipowicz...
Diagenesis in Modern, Danish, Burned Pig Bone
Publication Date
During archaeological excavations, burned bones are often found as a result of cremation, cooking or accidental fire. Even though the bones are burned, their elemental composition might still hold information about diet, habitat and health history in the past.
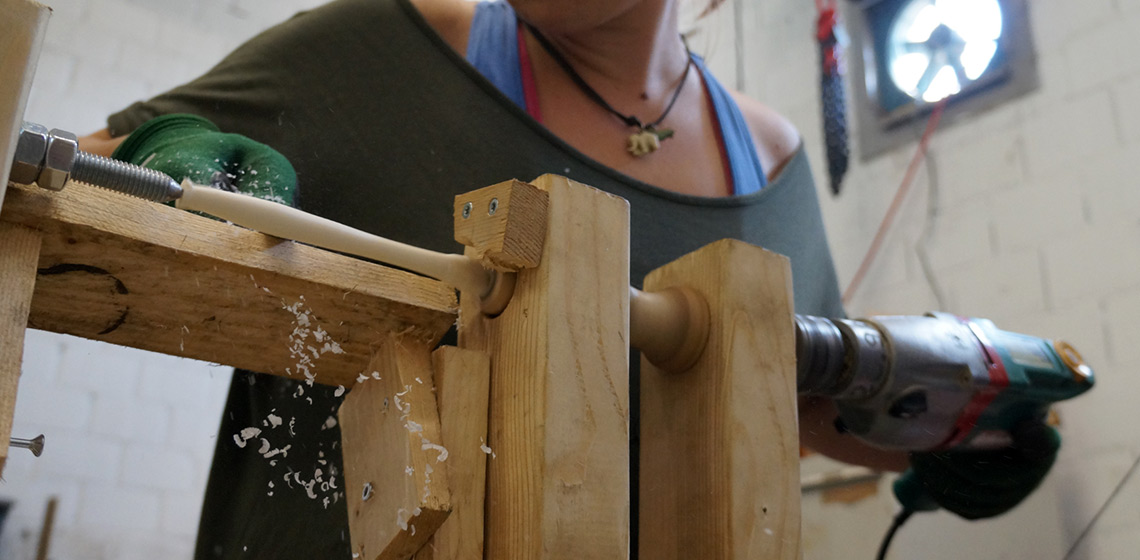
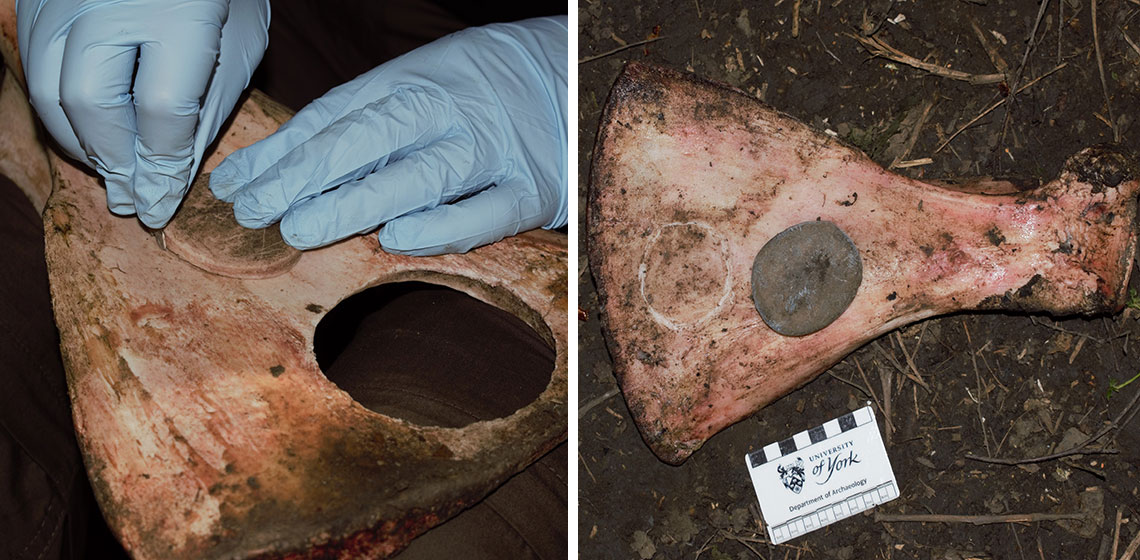
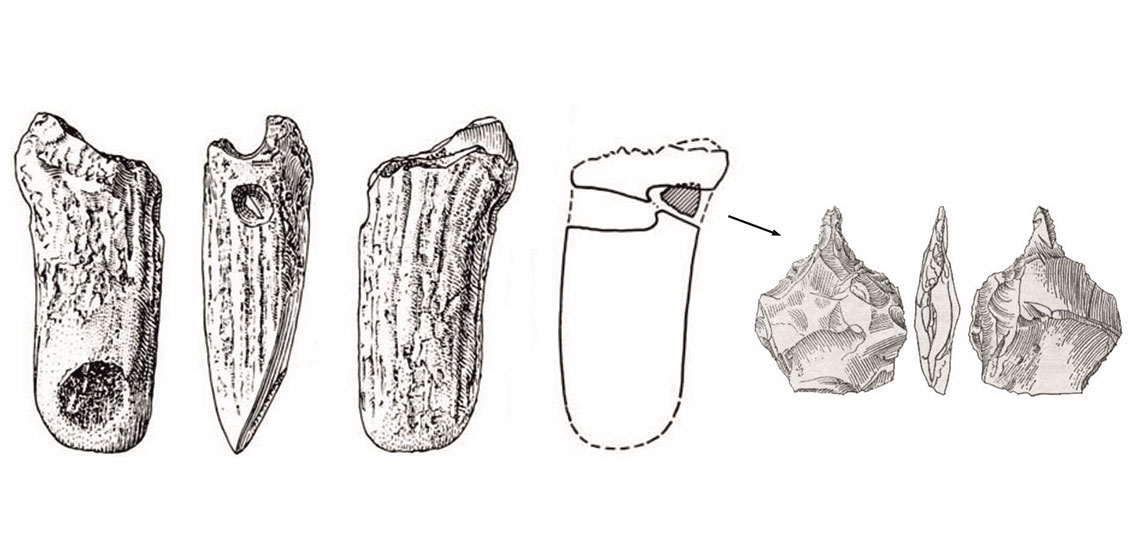
How Did They Drill That? – A Few Observations on the Possible Methods for Making Large-sized Holes in Antler
Publication Date
From the Neolithic period comes a whole range of various kinds of artefacts made of antler (for example axes, hammer-adzes), distinguished by the presence of a large hole (diameter over 2 cm) in their structure. With time, archaeologists started to wonder about possible ways of producing holes of this type...
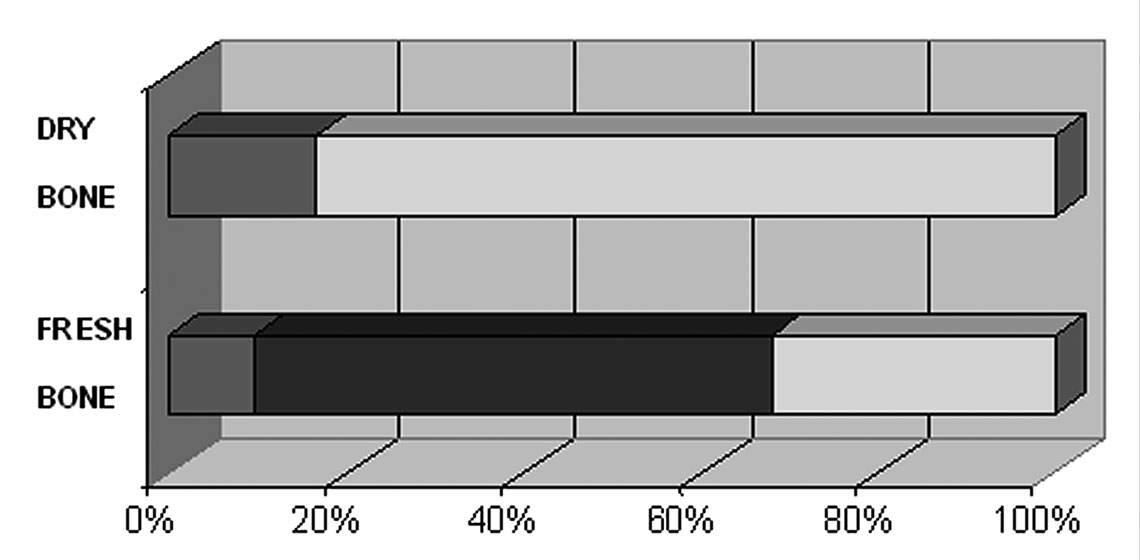
An Experimental Programme for the Collection and Use of Retouching Tools Made on Diaphyseal Bone Splinters
Publication Date
The present work presents the results of 38 experiments of bone fragmentation and blank collection, together with 177 experiments of retouch. In the first series of experiments, the fragmentation step was executed by massive percussion using macro-lithic tools...