EXARC Journal Issue 2021/4



17 Articles | DOAJ | Open Access
ISSN: 2212-8956
Publishing date: November 25, 2021
📄 EXARC Journal 2021/4 Table of Contents
Copyrights: EXARC, 2021
Summary
The EXARC Journal 2021/4 was published in November and contains 13 reviewed and 4 unreviewed articles. As always, all articles are open access.
Four of the reviewed articles have been presented at the EAC 12 World Tour this year and are now available in the journal. Dzwiza looks at Ancient Technologies in Contexts of the Sustainable Development Goals, Palmer investigates the weaving of an Ancient Greek chlamys; Durante, Stellacci, Pellegrini, de Angelis and Scacchetti evaluate the production and possible uses of deer antler tools in Italy and Ertl and Yoshida look at the Approaches to Experimental Pit House Reconstructions in the Japanese Central Highlands. There are three articles on medieval bone pipes in this issue from different geographical regions – Finland (Rainio, Tamboer and Saarikivi), Poland (Popławska, Kander-Marchewka, Skibińska and Zawadzki) and England (Taylor) – investigating the tones and sounds of these musical instruments through reconstruction. Rose, Fabian and Goren will shed light on the pure copper metallurgy of the Chalcolithic Southern Levant, Stasińska offers an insight into the textile dyeing process in Anglo-Saxon and Anglo-Scandinavian Britain, Cetwińska and Sadło let us in on their experiment to “verify the effect of adding beeswax to the adhesives.” A new approach to Roman bone artefacts is investigated in the article by Müller, Dreschler-Erb and Wojtczak. Baker, Scott, Gethin and Sinclair are introducing their pilot study on birch bark glue in Neanderthal clothing while Taylor proposes a new appearance of the iron stand from Sutton Hoo.
The unreviewed mixed matter articles look at book and event reviews. The first one discusses the Vorgeschichtliche Techniken im Archäologischen Experiment (prehistoric techniques in archaeological experiments) in the museum in Dithmarschen by Rüdiger Kelm and Birte Meller; the second review looks at the papers from the UISPP Congress in Florianópolis, Brazil published in an anthology and the third article reviews Native American Blowguns by Douglas S. Meyer. The last article in the mixed matter section reviewed the conference Novilara dei Piceni (Walk like a Picenian) which took place in Italy at the beginning of October this year.
Reviewed Articles
Ancient Technologies in Contexts of the Sustainable Development Goals
***The demand for innovative solutions to pressing ecological and societal challenges is on a constant rise. Ancient technologies provide extensive yet underutilized opportunities to help solve such problems. This paper presents three of these technologies and their successful application in modern contexts based on five illustrating case studies...
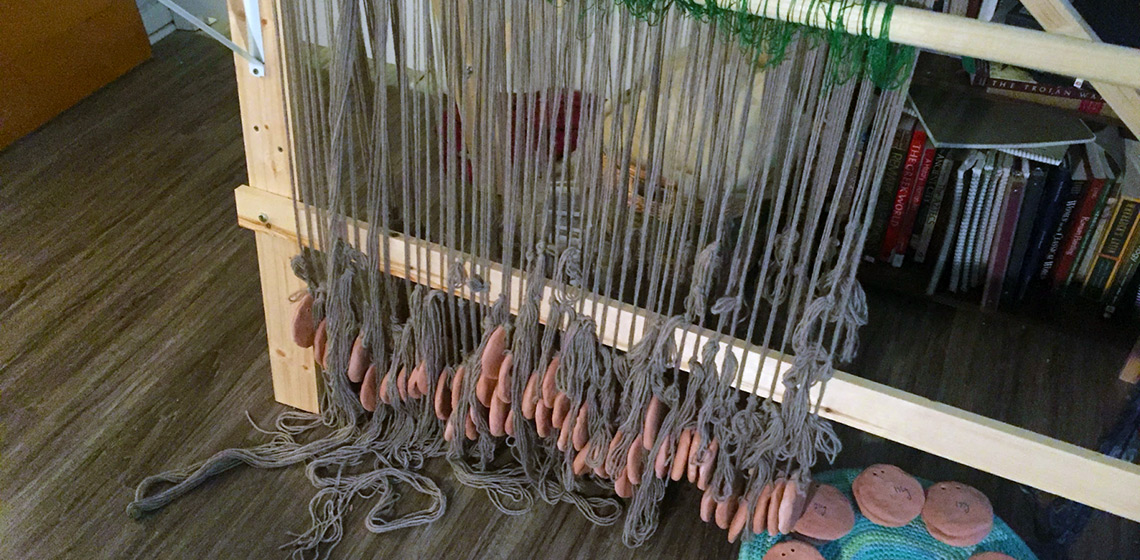
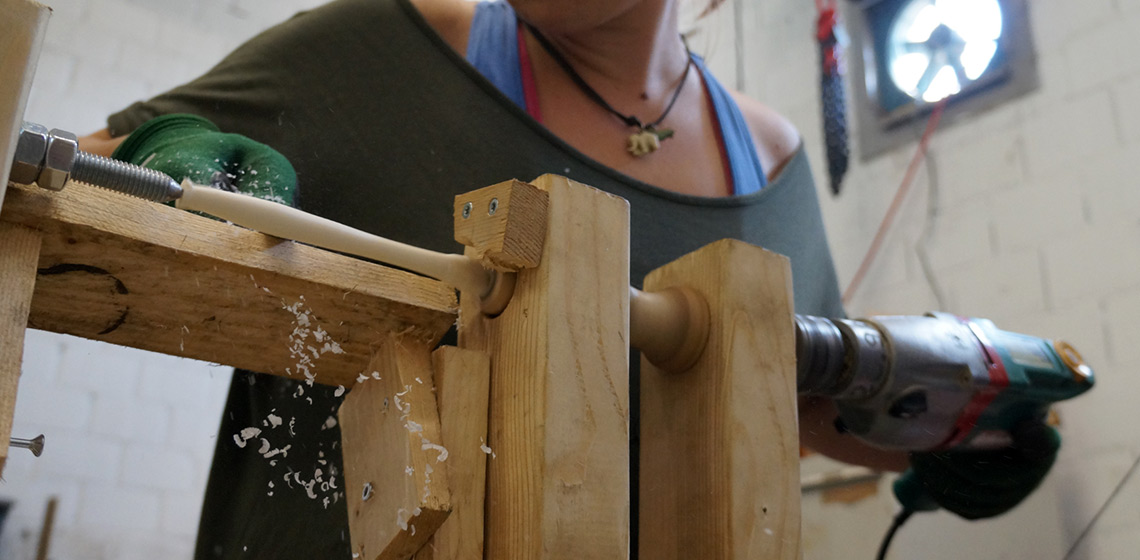
Ancient Greek Weaving, Experimental Archeology on Greek Textiles and Household GDP
***This paper outlines the experimental weaving project of an ancient Greek chlamys to investigate the weaving production capacity of a typical household and reconstruct women’s contribution to household GDP in ancient Greece. While some scholars have researched finer textiles and tech-niques based on visual evidence...
A Proposed New Appearance of the Iron Stand from Sutton Hoo, Based on Existing Material
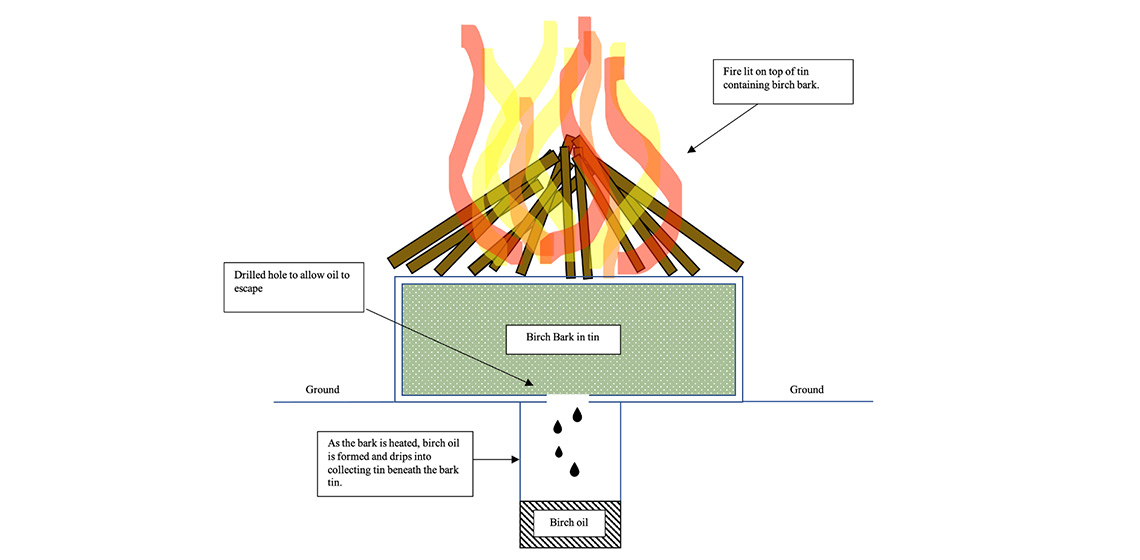
Birch Bark Glue and its Potential Use in Neanderthal Clothing: A Pilot Study
Roman Bone Artefacts – First Steps Towards a New Approach
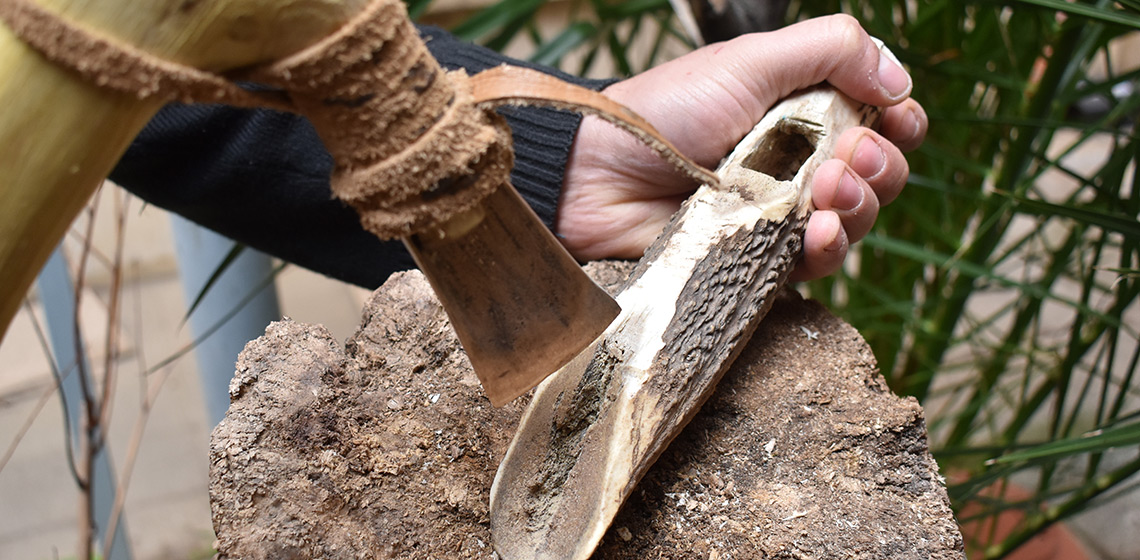
Hoes or Adzes? Experimental Reproduction and Uses of Deer Antler Tools from the Bronze Age Terramara of Pragatto (Italy)
***This research aimed to evaluate the hypotheses related to the production and possible uses of a class of deer antler tools from the Bronze Age Terramara of Pragatto (Italy). These bevel-ended instruments are traditionally considered handled hoes, related to agricultural purposes such as tillage...
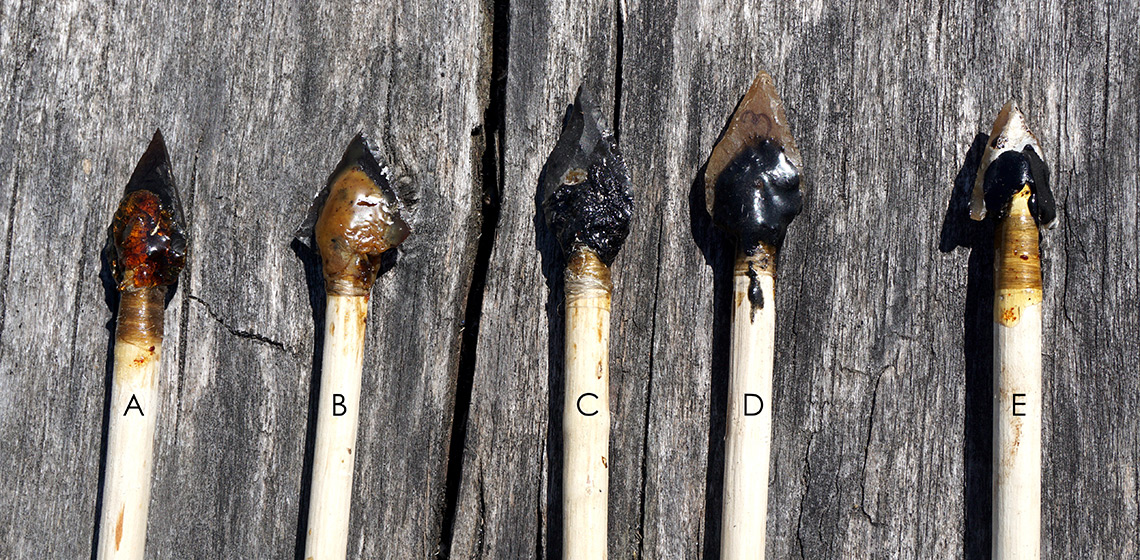
Beeswax an Addition to the Production of European Stone Age Adhesives
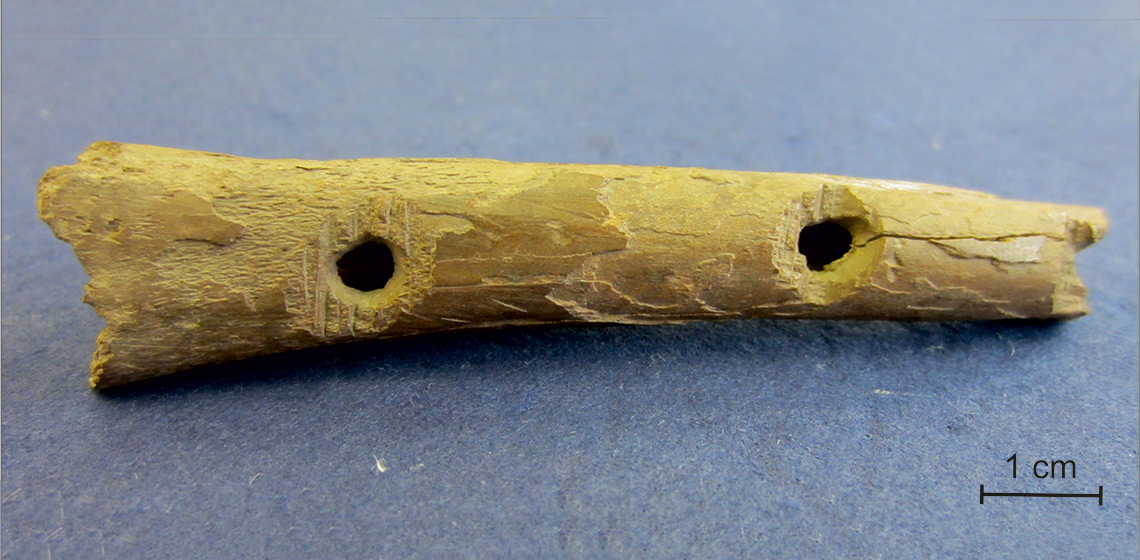
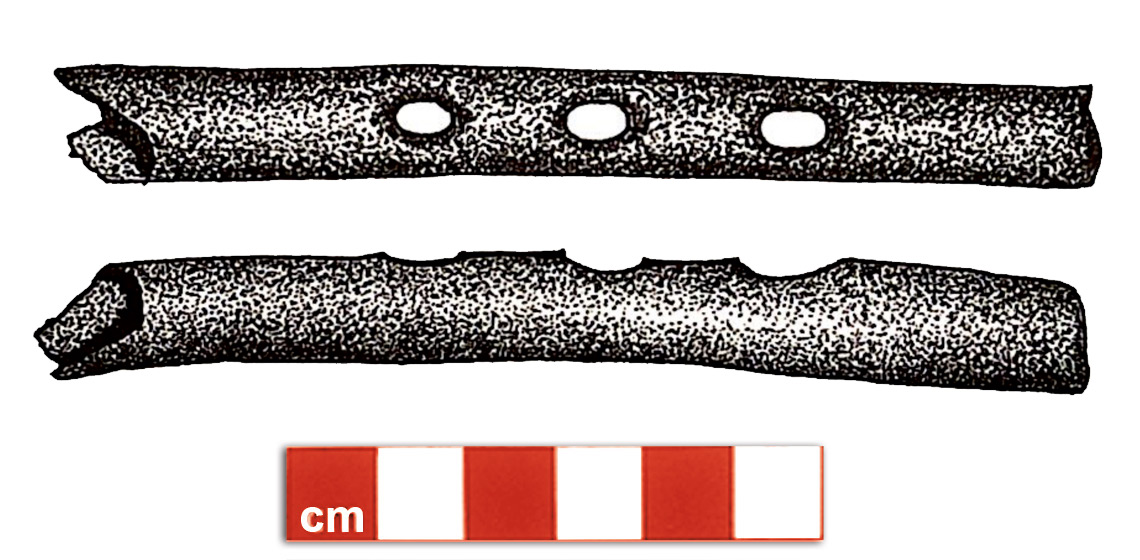
A Singing Bone from the Mätäjärvi (‘Rotten Lake’) Quarter of Medieval Turku, Finland: Experimental Reconstructions and Contemporary Musical Exploration
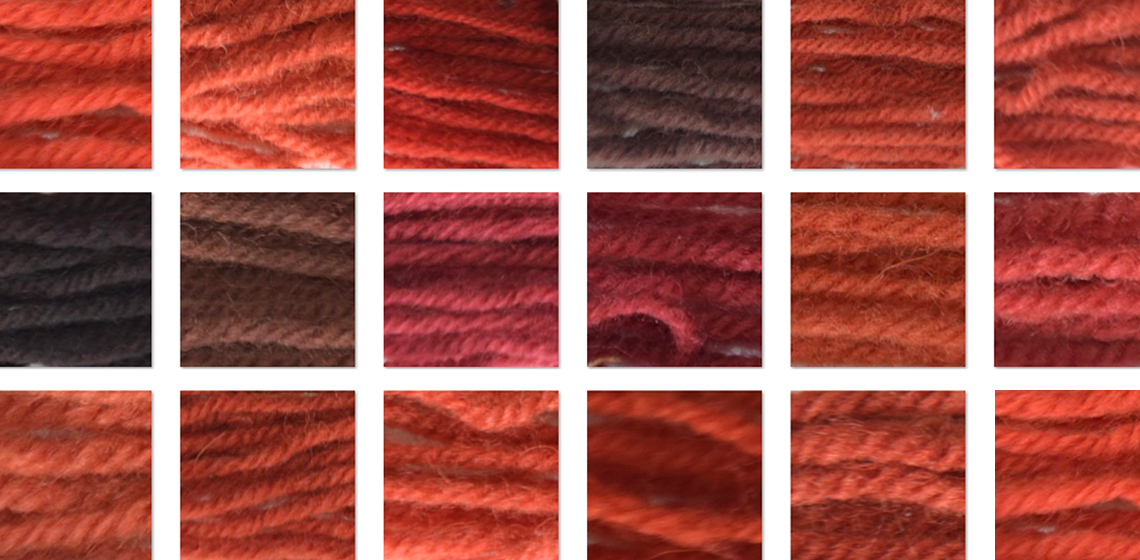
Before They Dyed. Mordants and Assists in the Textile Dyeing Process in Anglo-Saxon and Anglo-Scandinavian Britain: An Experimental Approach
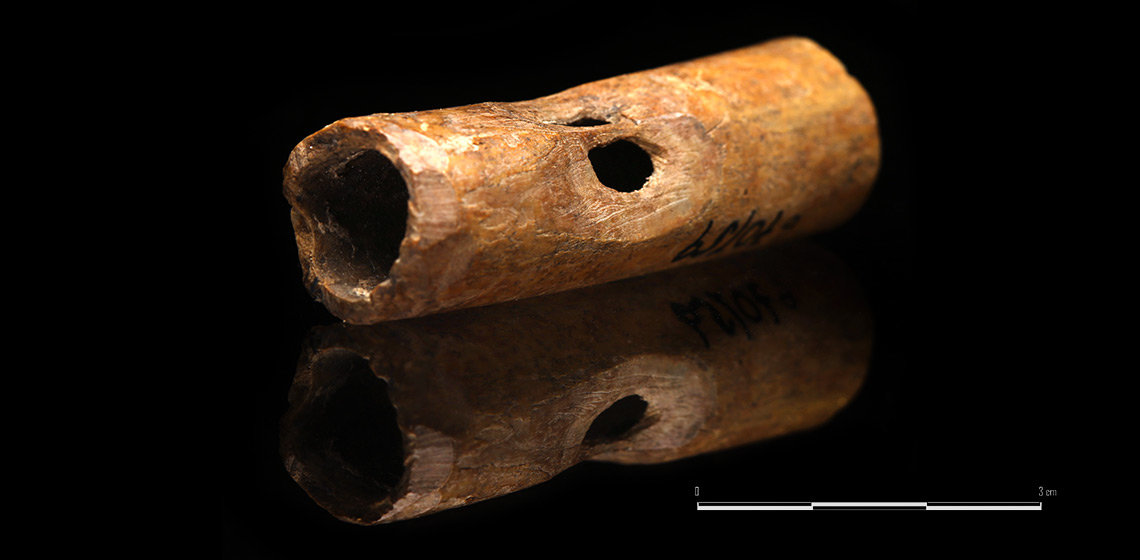
Bone Pipes with Parallel Tone Holes. Materials from Medieval Poland (until the End of the 12th C)
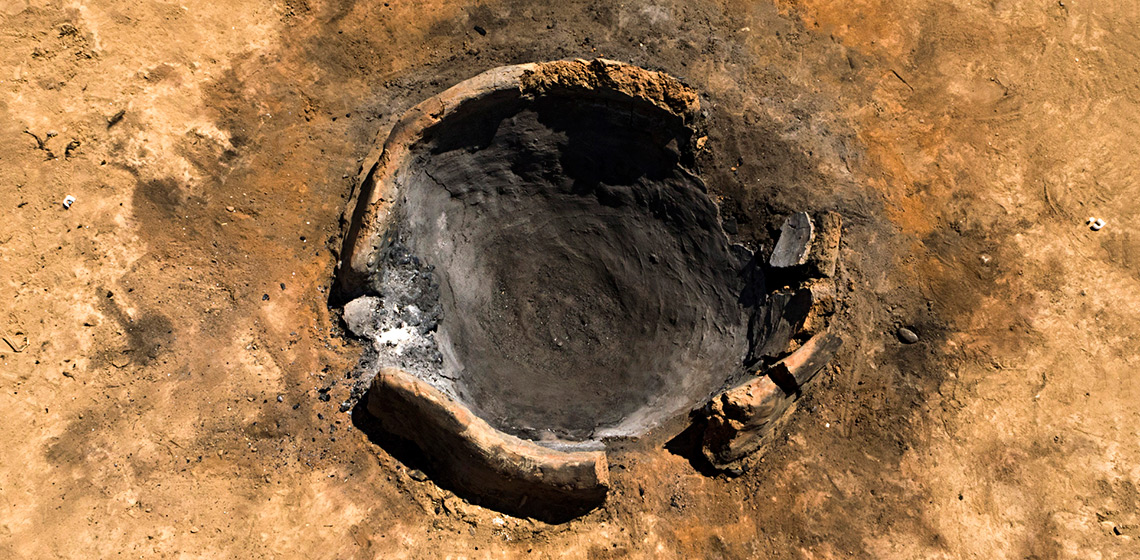
Shedding New Light on the Pure Copper Metallurgy of the Chalcolithic Southern Levant Through an Archaeological Experiment
Early Medieval Bone Pipes: Understanding the Sounds of These Instruments through Reconstruction
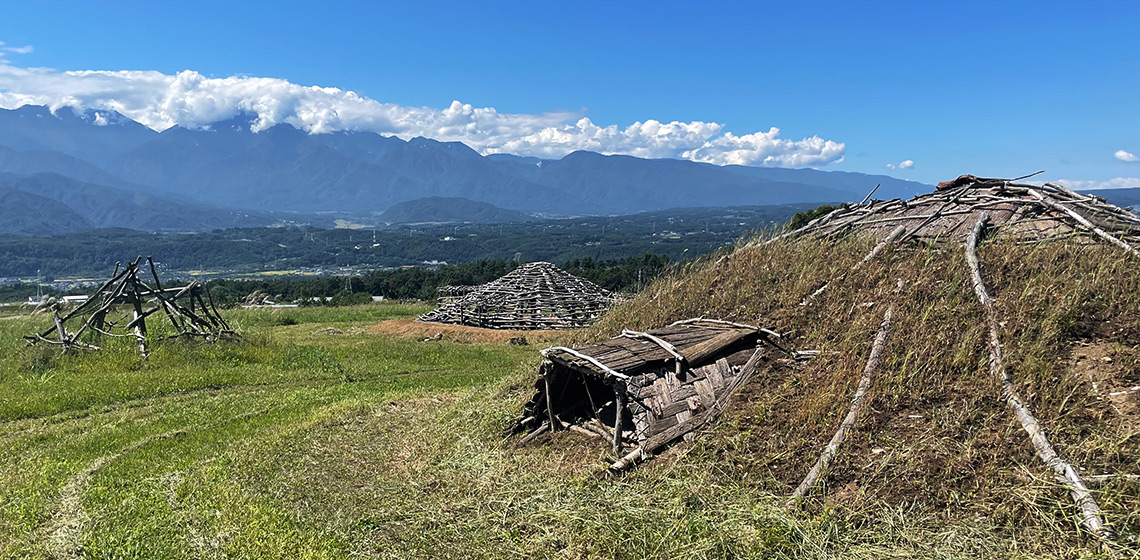
Approaches to Experimental Pit House Reconstructions in the Japanese Central Highlands: Architectural History, Community Archaeology and Ethnology
***In Japan, over 1,000 prehistoric house reconstructions have been built at 360 different locations since 1949. Pit houses from Neolithic Jomon Period (14,000–300BC) are the most common but they are mostly based on archaeological remains limited to pits and postholes. Therefore, decisions on material and structure come from various sources, some based on research and others rooted in cultural ideologies or individual’s preferences...