The content is published under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license.
Themed Collections:
Textiles

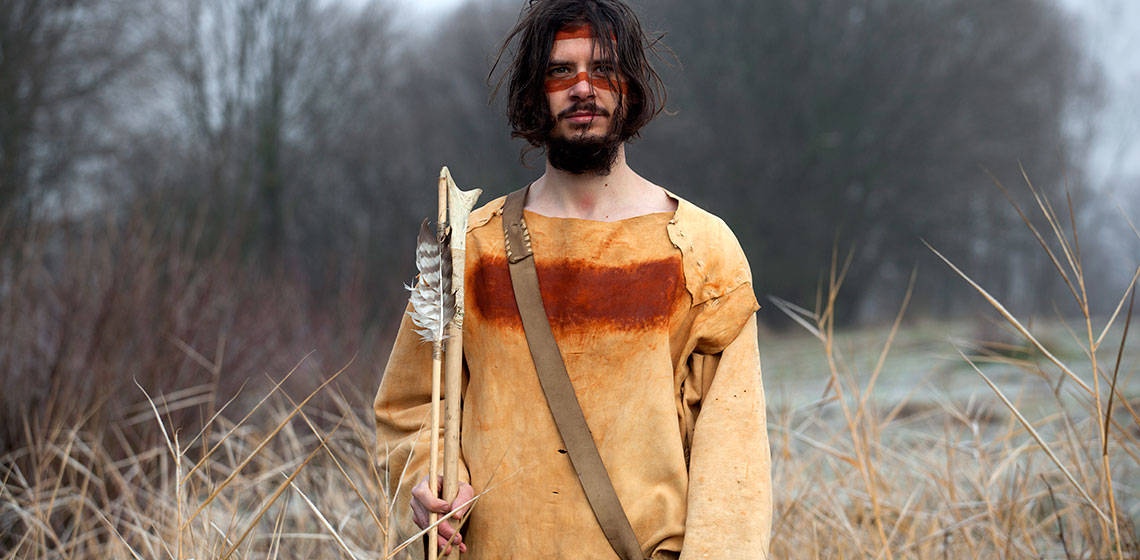
Textiles do not often appear in archaeological excavations. We find them in stable situations, for example completely under water or in desert like circumstances. When archaeologists do find textile remains, there usually is a lot of information we can derive from those. It says something about their users, about the availability of material and for example colours. But even if we don’t find textiles themselves, we can often find traces or derivatives, think of textile prints in pottery, or tools used in the production process like spinning weights. There is more than meets the eye, and it is here that experimental archaeology comes in.
Featured
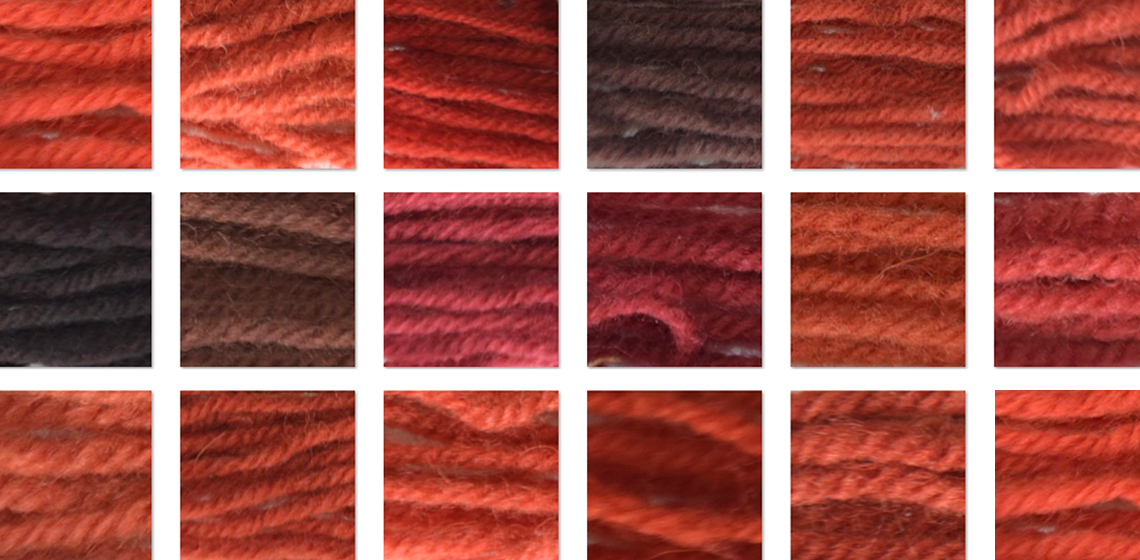
Adventures in Woad: Woad Dyeing in the Ancient, Medieval, and Modern Worlds
Olives as a Dye for Wool Textiles
Shaping Minoan Clay Tablets and Hanging Nodules: Contributions from Experimental Research and X-radiography
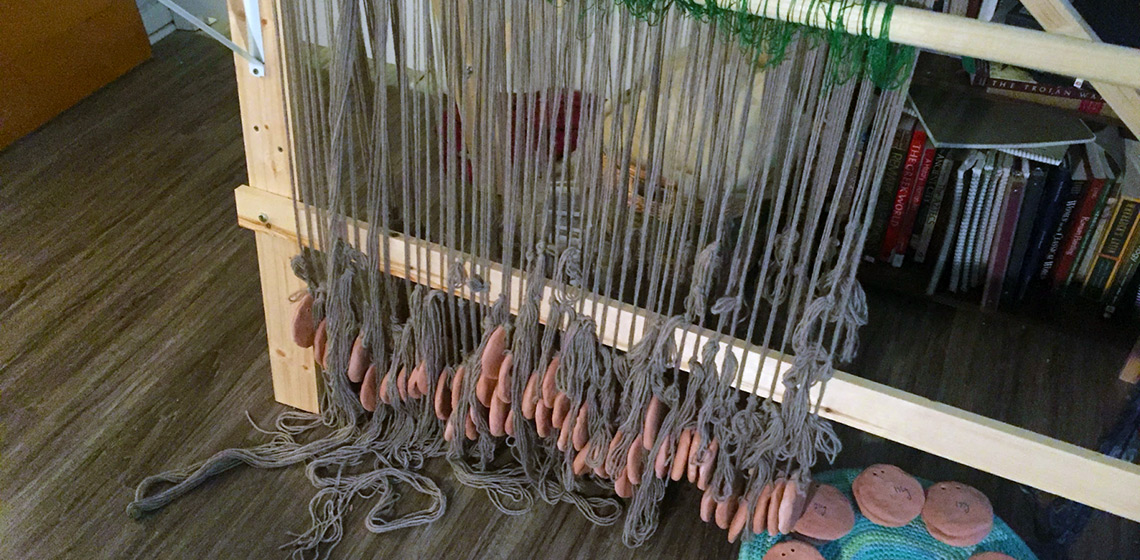
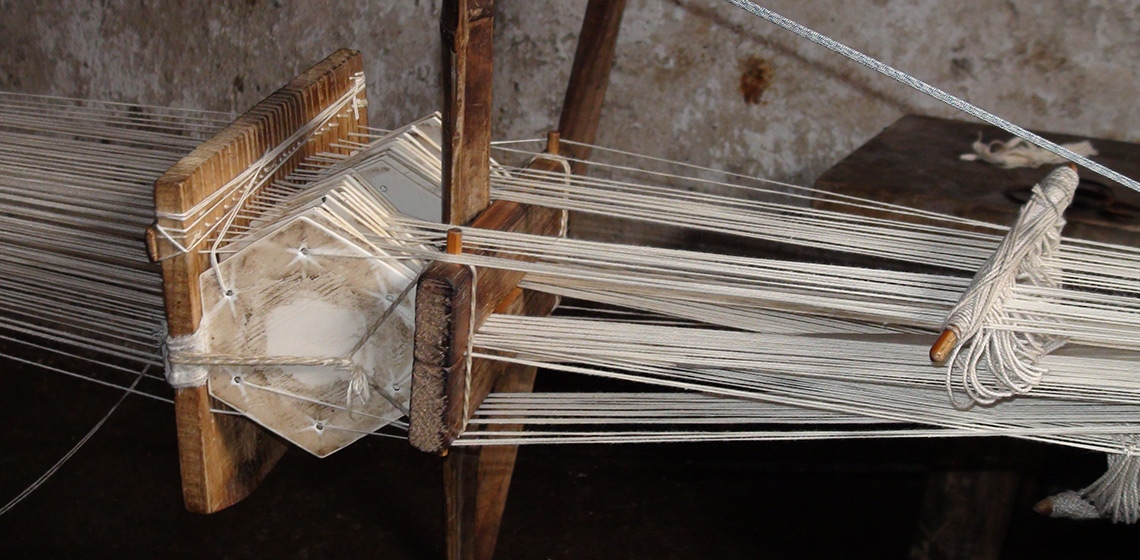
Is it Possible to Weave 8.end Satin with 5 Rods on a Warp-weighted Loom?
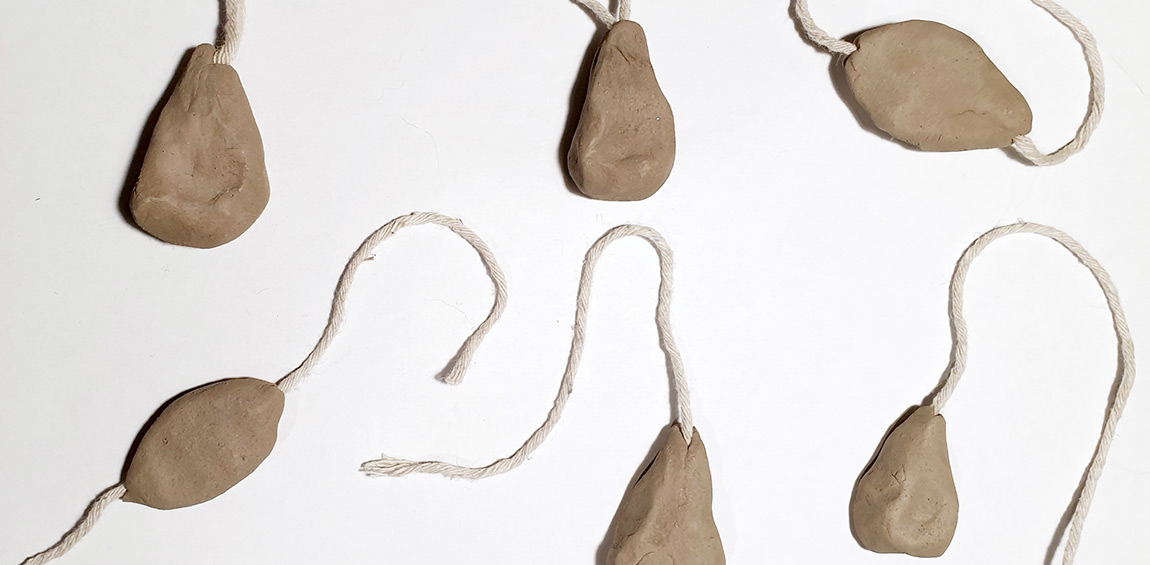
Experimental Weaving and Twining with Ceramic Crescents from the Late Neolithic and Chalcolithic in Southwestern Iberia
Function Follows Form: Assessing the Functionality of Shells and Greenstone Shell Effigies as Formative Period Mesoamerican Textile Fabrication Tools, Part 1: Tagelus plebeius Atlantic Stout Razor Clam Shells
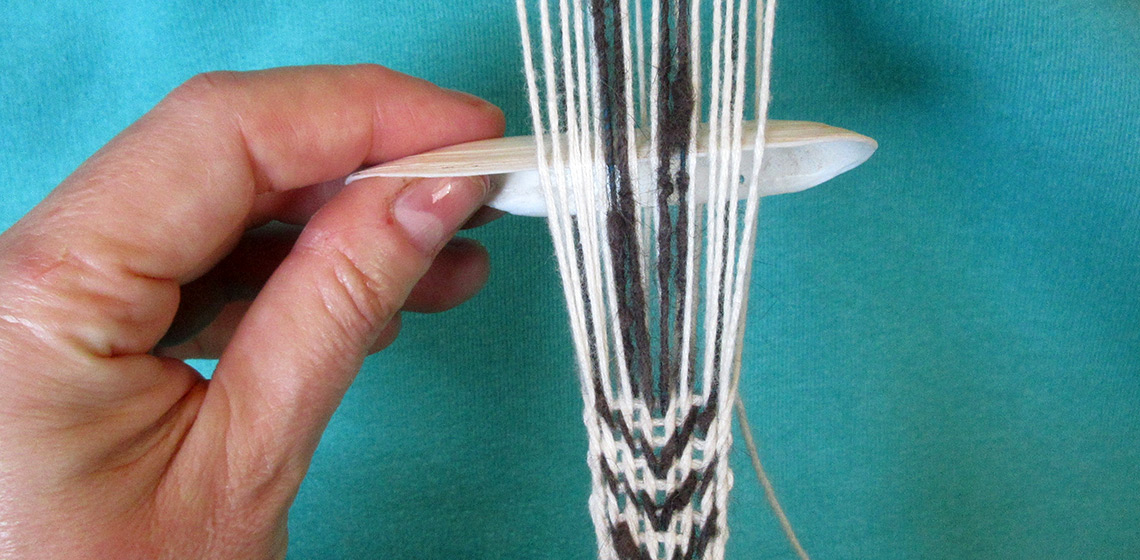
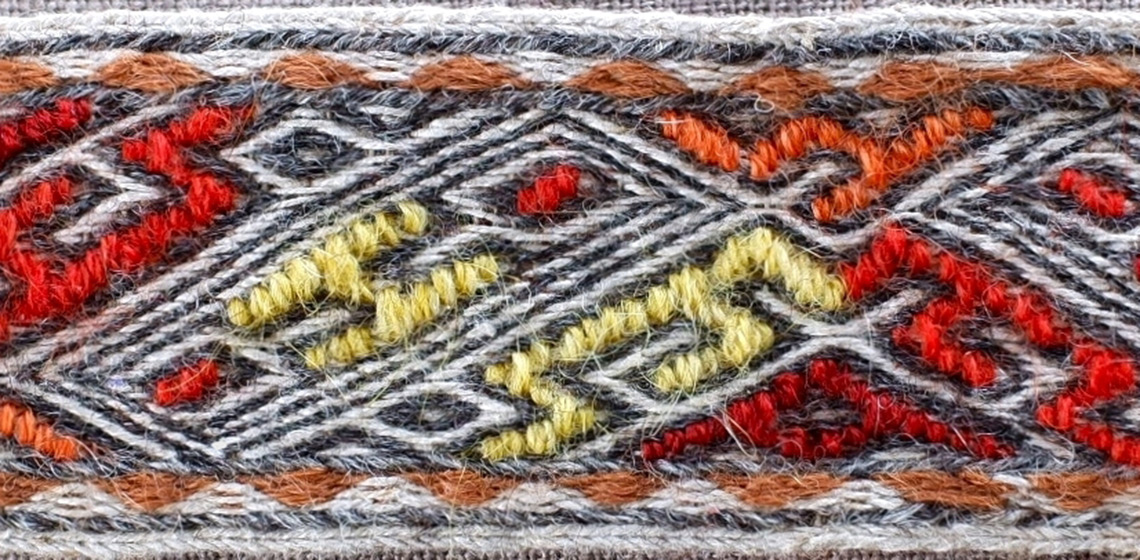
A Tablet Woven Band from the Oseberg Grave: Interpretation of Motif and Technique
Ancient Greek Weaving, Experimental Archeology on Greek Textiles and Household GDP
***This paper outlines the experimental weaving project of an ancient Greek chlamys to investigate the weaving production capacity of a typical household and reconstruct women’s contribution to household GDP in ancient Greece. While some scholars have researched finer textiles and tech-niques based on visual evidence...
Before They Dyed. Mordants and Assists in the Textile Dyeing Process in Anglo-Saxon and Anglo-Scandinavian Britain: An Experimental Approach
More Testing of Mesoamerican Lunate Artifacts as Possible Loom Weights, that also Functioned as Twining Tools
Bast, Ferns, and Mud: Experimental Recreation of a Kapa Kaha (Barkcloth)
***Kapa (Hawaiian barkcloth) was the ubiquitous fabric of historic Hawaiʻi, used for everything from clothing to bedding, from swaddling newborns to enshrouding the deceased, and all things in between. This textile is crafted from the bast (inner bark) of several plant species...
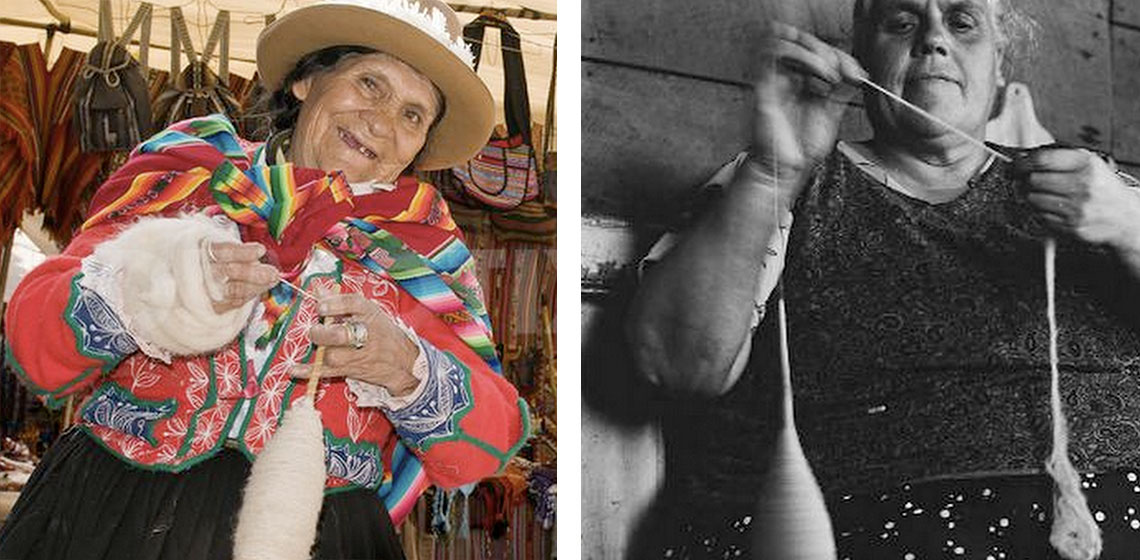
Recreating Historic European Spindle Spinning
A Discussion on the Position of Weaving in the Society of Prehistoric Britain
Just how practical is it to Move a Warp-weighted Loom from between the Interior and Exterior of a Roundhouse?
Weaving Production in Butser Ancient Farm Roundhouses in the South of England
A Shared Warp: The Woven Belts of the Lao Han People, China
The renowned weaver Peter Collingwood briefly mentioned such belts in his book The Techniques of Tablet Weaving (Collingwood, 1982, pp.219-220). Not long before he died in 2008, he contributed a couple of pages on these belts to the book Minority Textile Techniques: Costumes from South-West China (Collingwood, 2007, pp.28-29).
What was *platъ and how Did it Work? Reconstructing a Piece of Slavic Cloth Currency
The Shroud of Turin and the Extra Sheds of Warping Threads. How Hard can it be to Set up a 3/1 Chevron Twill, Herringbone on a Warp-weighted Loom?
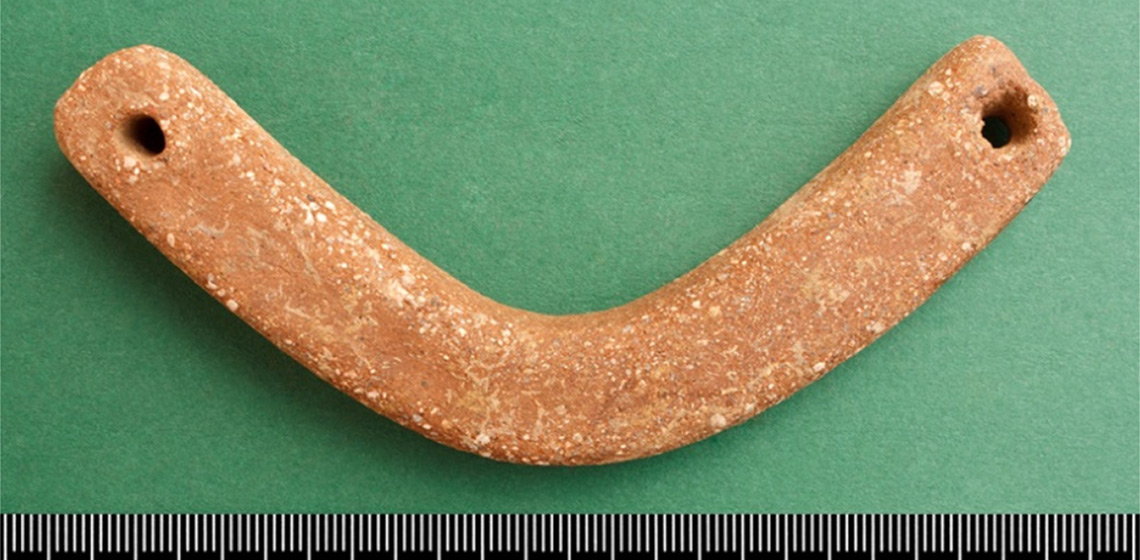
Groundstone Indications from the Southern Levant for a 7th Millennium BCE Upright Mat Loom
Testing Mesoamerican Lunate Artifacts as Possible Crescent Loom Weights
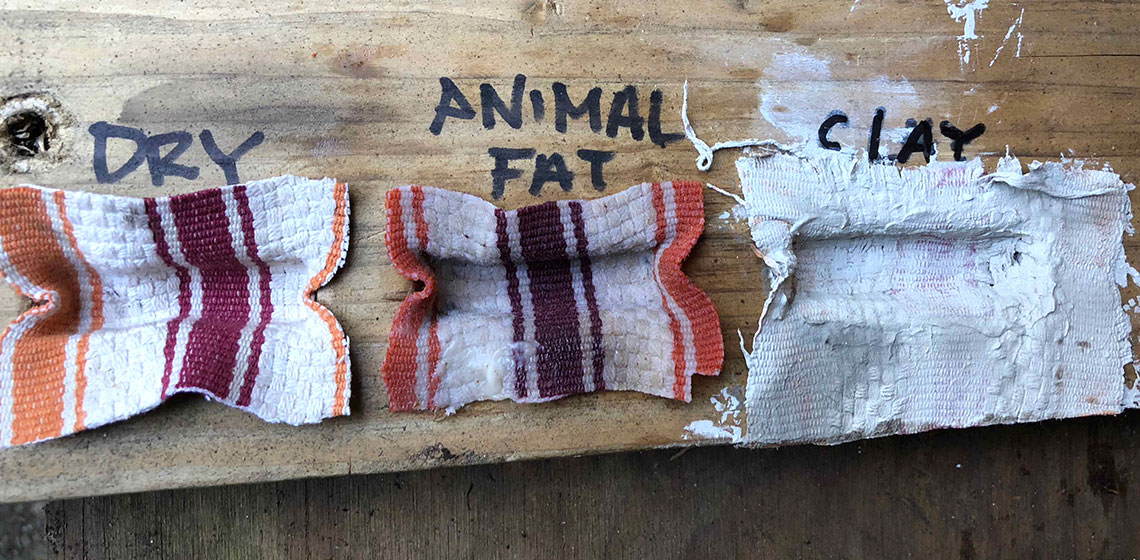
Flax Fibre Extraction Techniques in the Late Middle Ages
Working with Artisans; The ‘It Depends’ Dilemma
Replication of a Maori Ethnographic Textile Hem Border Pattern
***Replication of archaeological and ethnographic Māori textiles, under the direction of customary knowledge and previous practical experience, can provide a more nuanced understanding of the manufacture of taonga (treasures) made from fibre materials. A case study is presented here from the unique perspective of a weaver who...
The Contribution of Experimental Archaeology in Addressing the Analysis of Residues on Spindle-Whorls
***This contribution focuses on residues developing on spindle-whorls during spinning. Such a kind of tools is largely diffused in archaeological contexts where spindle-whorls were used in textile activities or deposited in burials as grave goods. Scholars recently approached the analysis of these objects through experimental archaeology to better understand their wide variation in size and shape especially in relationship with the adoption of...
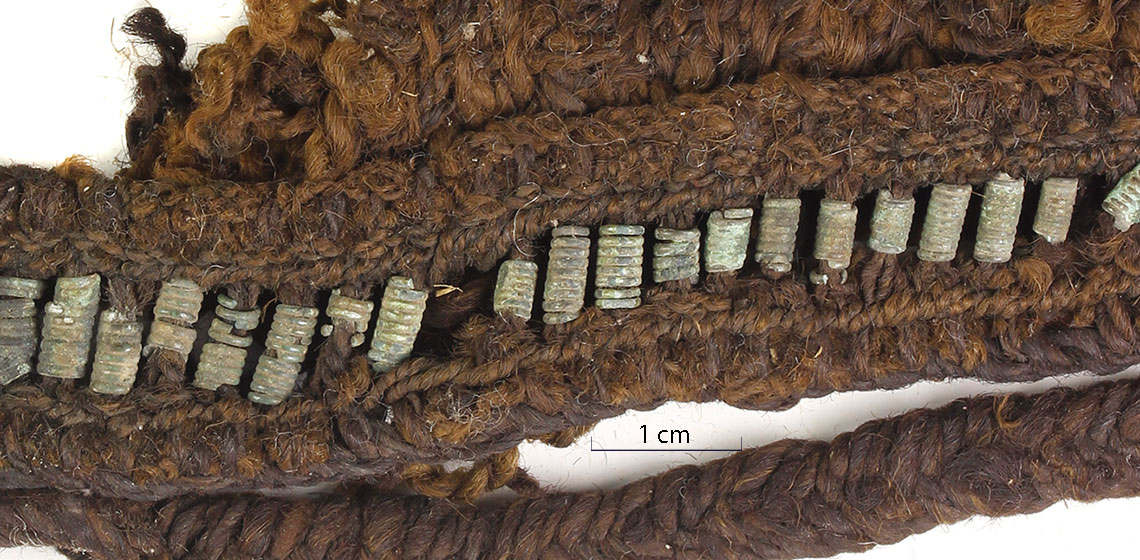
Textile Textured Silver Ingots: A Technical Investigation into how these Textures came to be on some Viking Hoard Ingots
Prehistoric Dressing for Third Millennium Visitors. The Reconstruction of Clothing for an Exhibition in the Liptov Museum in Ruzomberok (Slovakia)
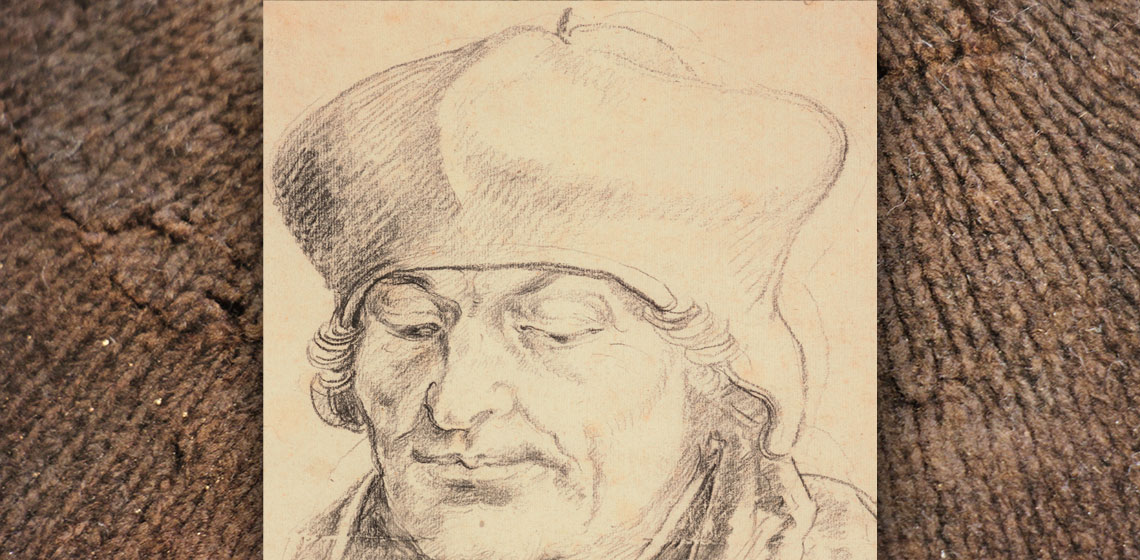
Some Uses of Experiment for Understanding Early Knitting and Erasmus' Bonnet
***Of Erasmus, prince of humanists (1466?-1536), no less than eight portraits from life survive – all eight in the exact same bonnet. A recently published investigation of this iconic garment (Kruseman, Sturtewagen and Malcolm-Davies, 2016) involved establishing a 250-year typology of the bonnet from iconographical sources, compiling technological and economic data from archival sources, and systematic experiments addressing numerous, various and fundamental questions, from yarn characteristics in archaeological knitted textiles to the use (or not) of hatter's forms in the finishing of bonnets.
Spiral Tube Decorations: a Thousand Years of Tradition
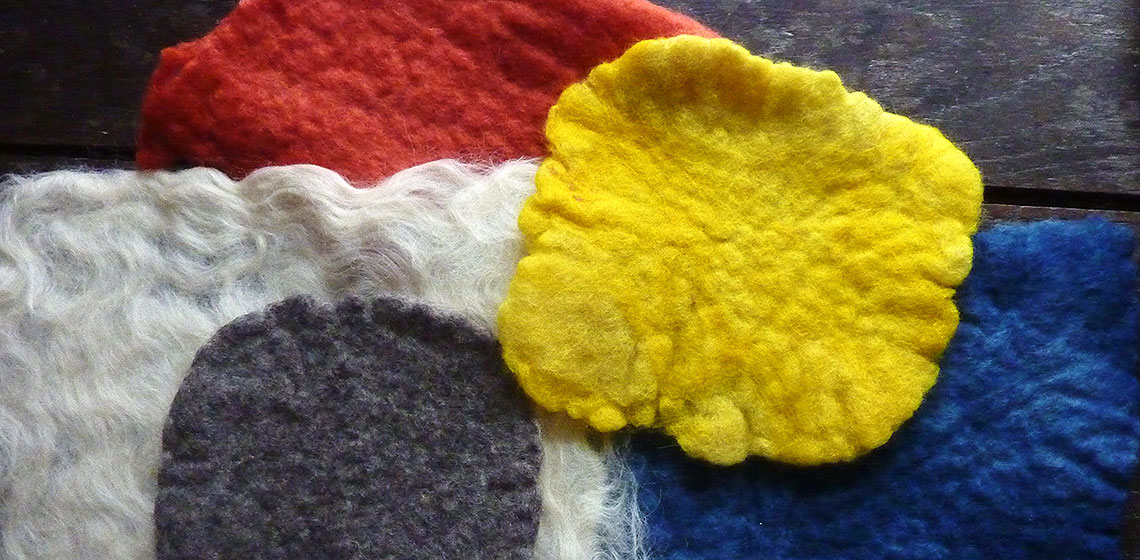
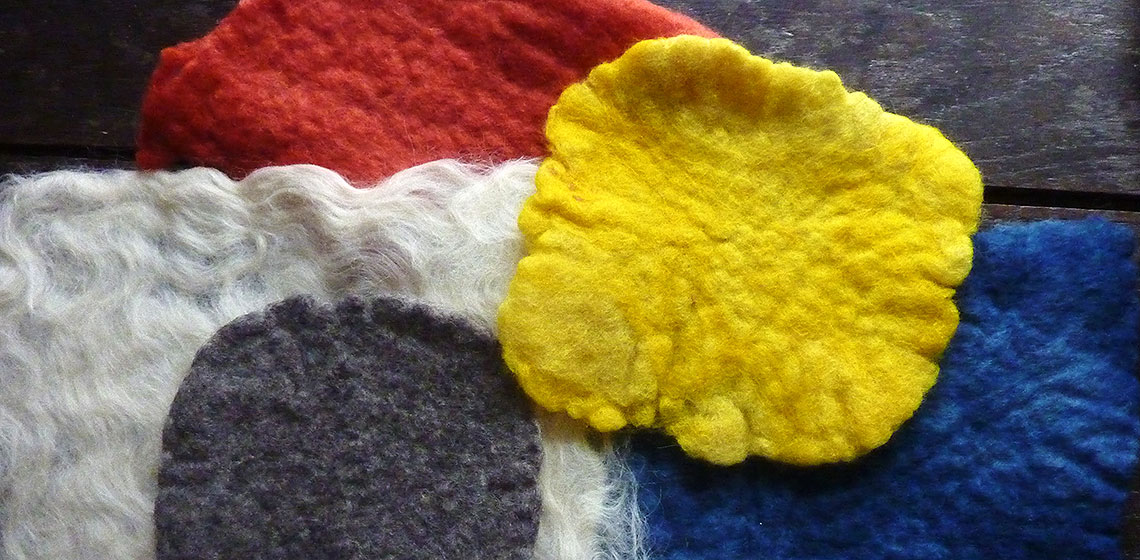
Needlework the Pazyryk Way?
My work has been inspired by some of the most remarkable textile finds - those in the Pazyryk kurgans (burial mounds) - specifically the felt shabraks (horse blankets). The detailed, intricate designs of these items are achieved by appliquéing felt on felt (sometimes leather is used) in a manner that adds both decoration and strength (See Figure 1) and is still used among the steppe-land nomads (Barber 1991, 220).
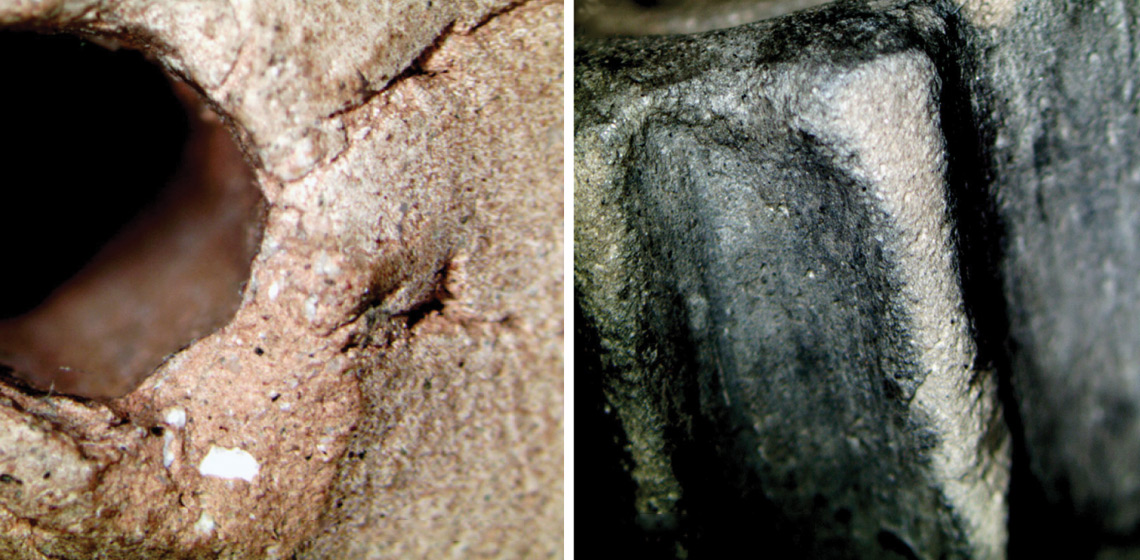
An Experimental Comparison of Impressions Made from Replicated Neolithic Linen and Bronze Age Woolen Textiles on Pottery
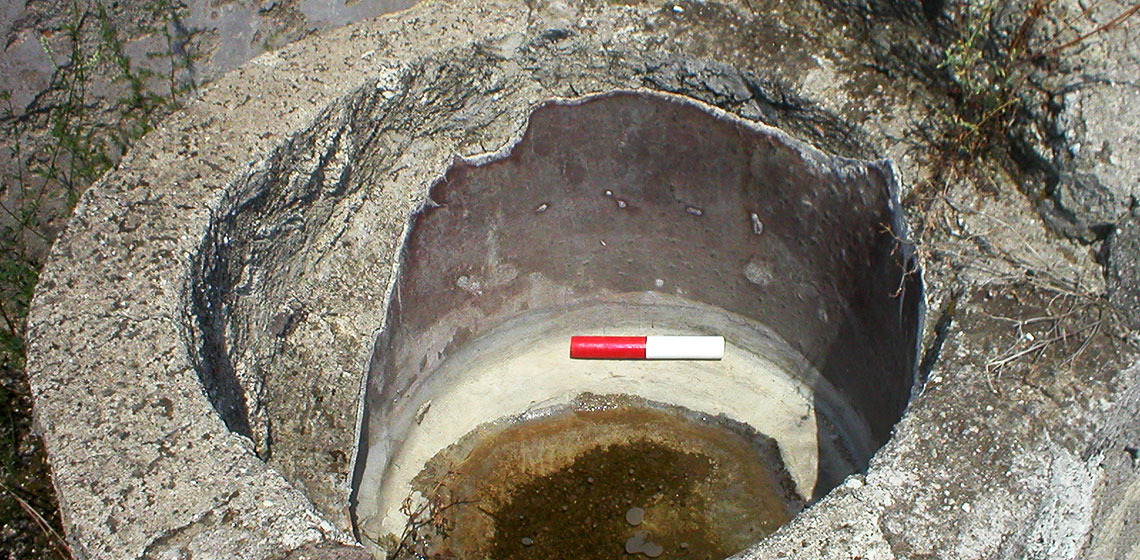
Investigating the Influence of the Kettle Material on Dyeing in the Industry of Pompeii
***Dyeing, especially in bright, intense colours, has been one of the methods used to embellish textiles and add to their value. A considerable dyeing industry can be shown to have existed in Pompeii. The city of Pompeii was destroyed in a volcanic eruption in AD 79, but its remains were preserved in situ...