Magyar Nemzeti Múzeum - Nemzeti Régészeti Intézet (HU)
The Hungarian National Museum was founded in 1802 and is the national museum for the history, art and archaeology of Hungary. It’s collections, exhibitions and affiliates present an overall view of the archaeology and history of the country.
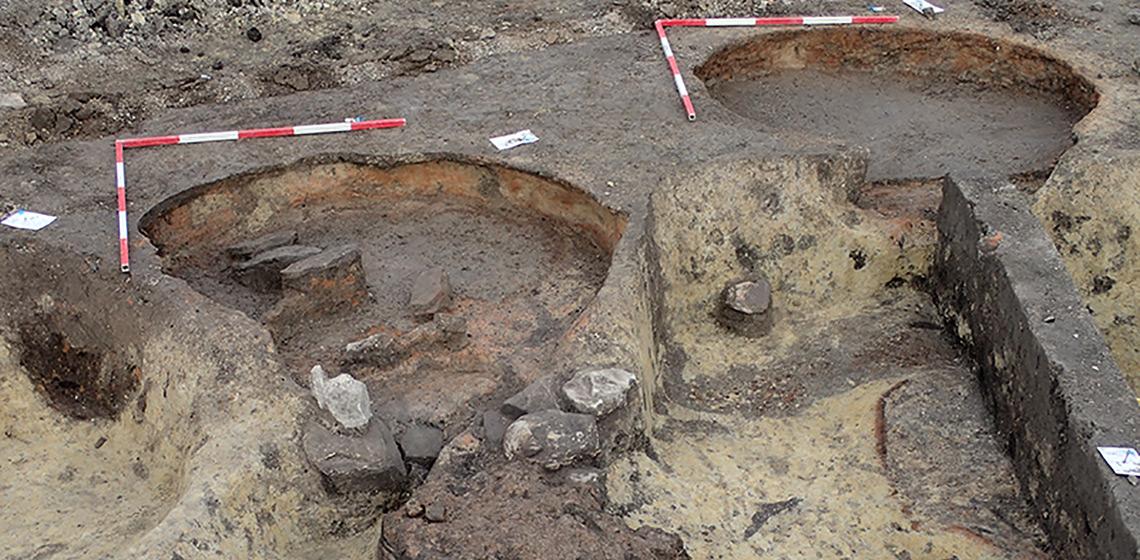
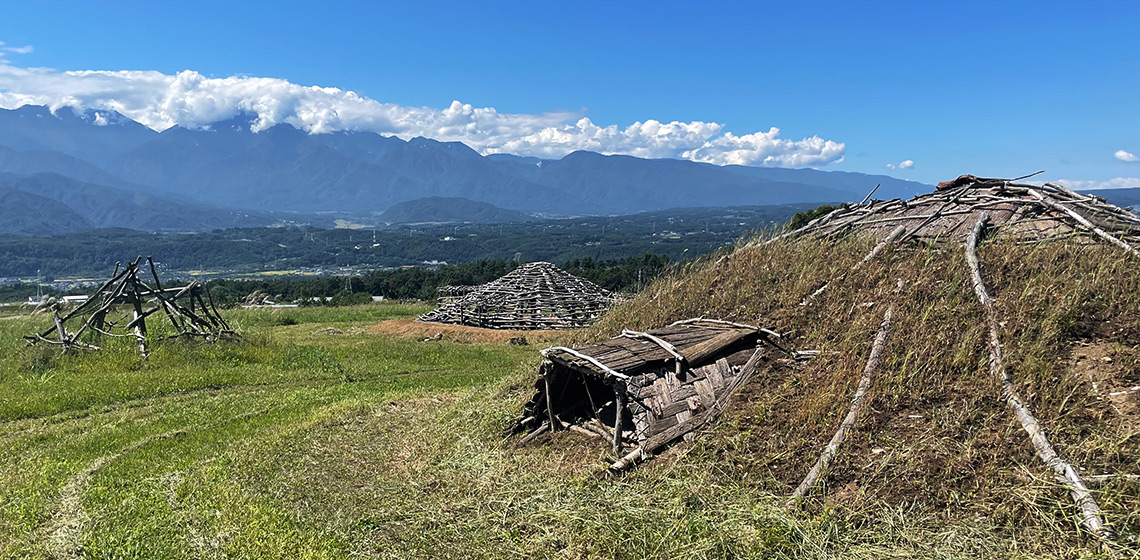
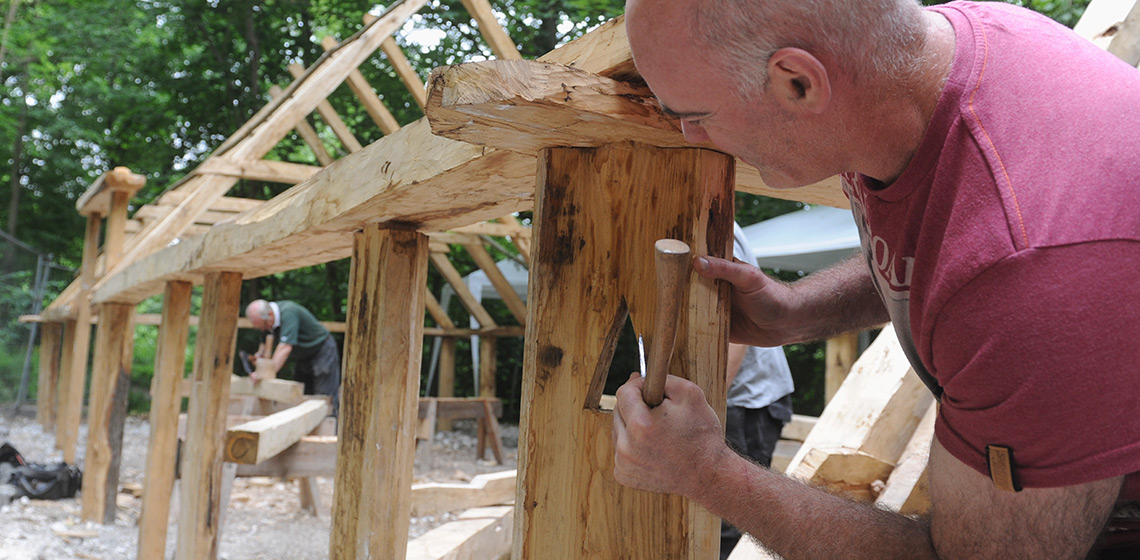
Until 2022 archaeological research, excavation work and presentation were assigned to two separate units within the National Museum. One of these was the Department of Archaeology, which conducts excavations and research of outstanding national significance (like for eg. Vértesszőlős, Kölked-Feketekapu, Heténypuszta, Zalavár, Doboz, Feldebrő, Gyula Castle, etc.). In addition to their research, the members of the department take part in university teaching and in the organisation of scientific life.