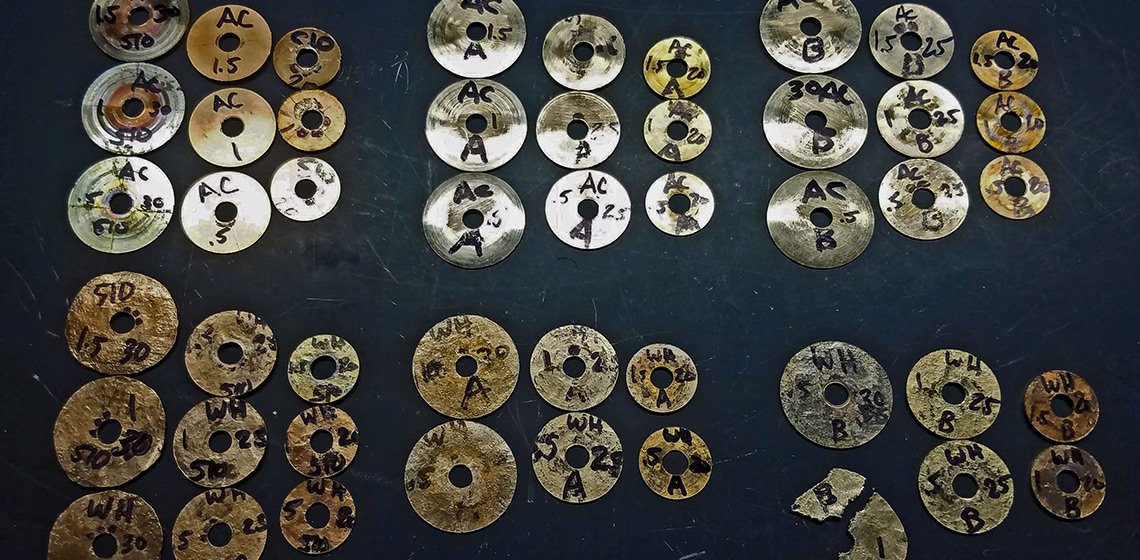
Drawing Wire
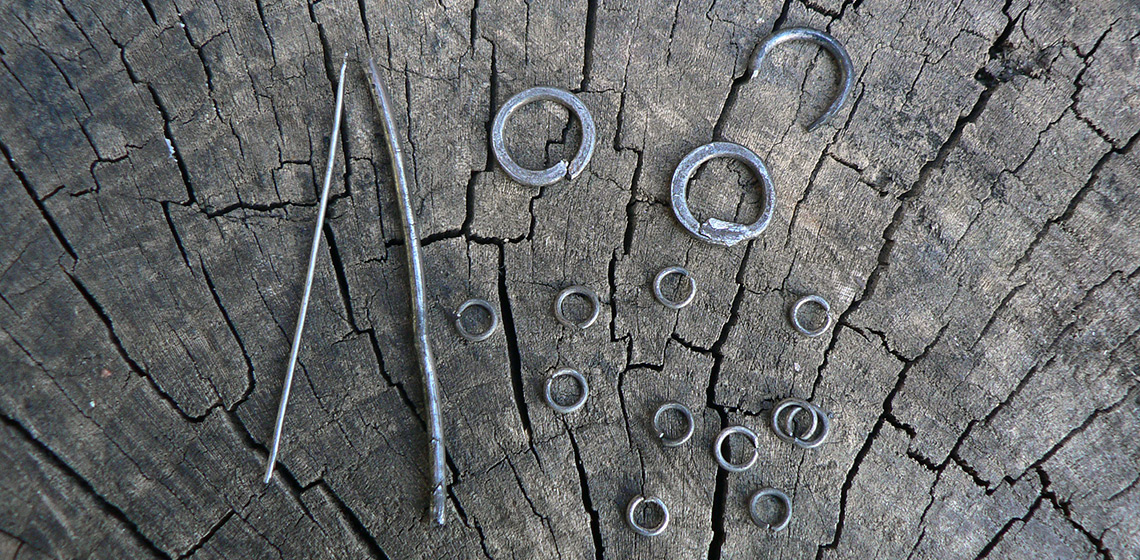
Chain mail
It is well known that in the Iron Age wire was made from gold, silver, and copper – but it is a relatively new realization in Northern Europe that wire was also extracted from bog iron ore. Metallurgical insight into how rings in chain mail are made, opened up the possibility of experimental archaeological experiments to learn how the process of making wire, as well as bending and welding it, was carried out in the Iron Age.