Experimental Archaeology of Iron Age Firing Structures from the Western Mediterranean
The TRANSCOMB project
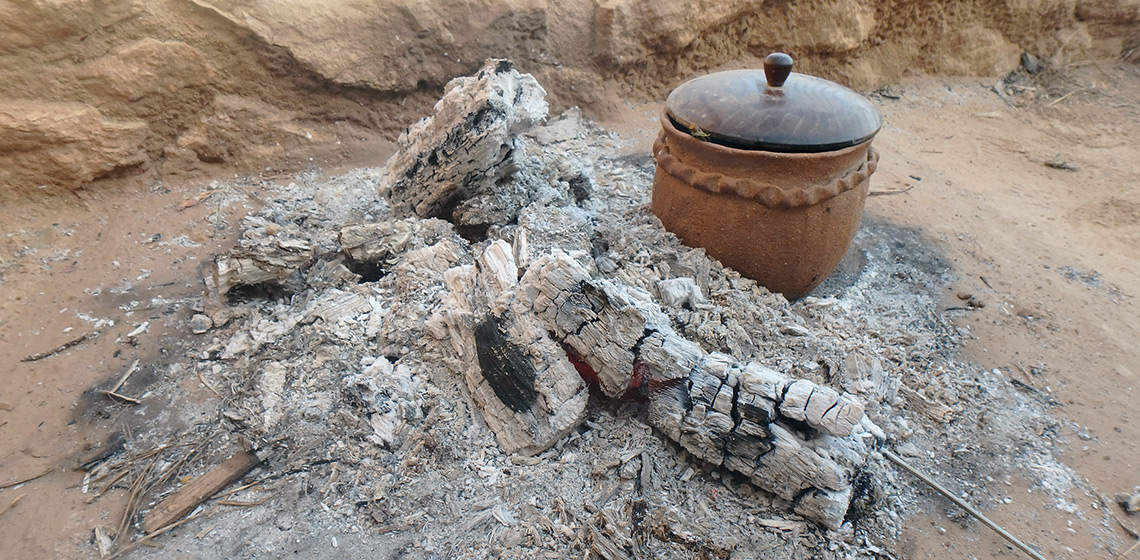
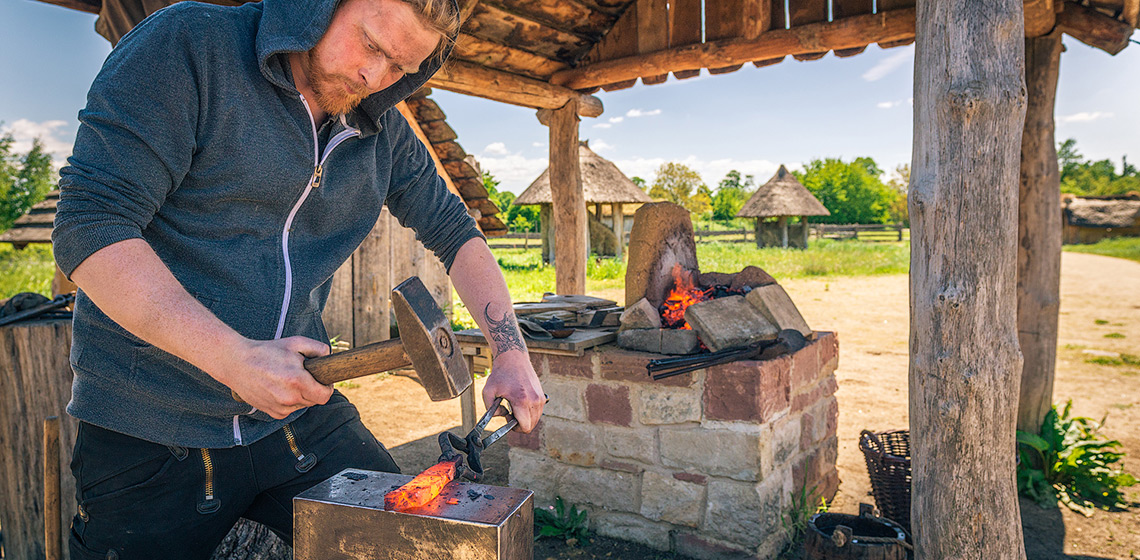
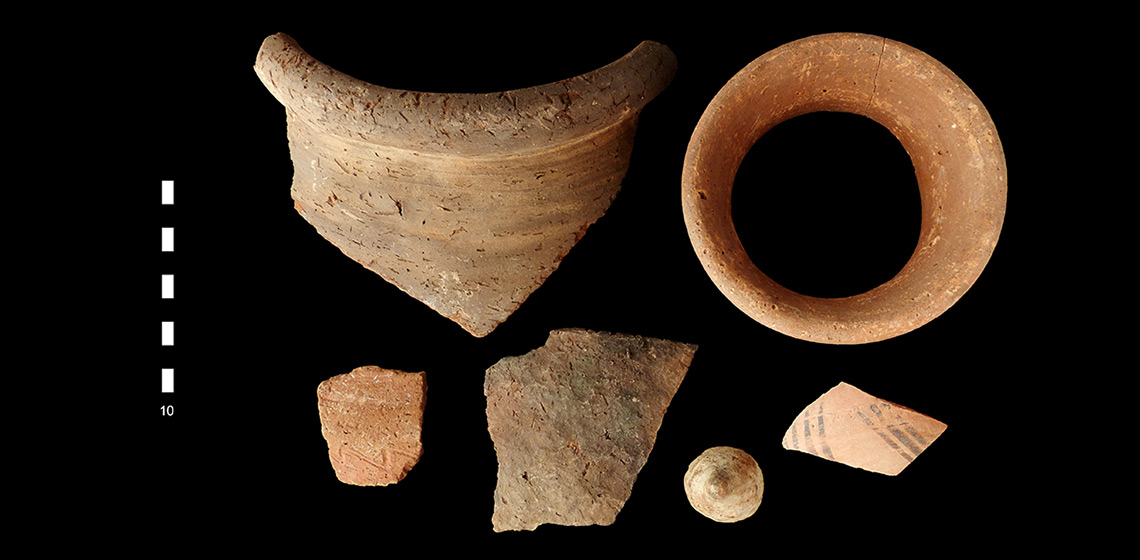
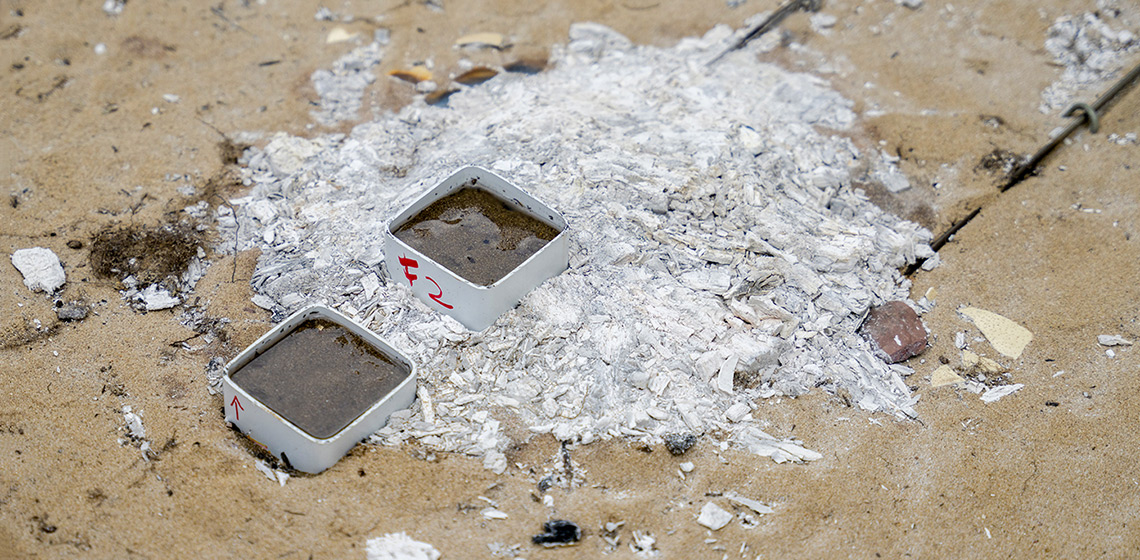
This research project, which started in 2020 and is funded by the Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation, is led by the Catalan Institute of Classical Archaeology (ICAC) and counts on the participation of about 20 researchers from different institutions. The project aims to analyse Iron Age combustion structures in the north-eastern Iberian Peninsula, the South of France, and the Balearic Islands (See Figure 1). The main aim is to obtain data about the functioning and efficiency of these structures during a range of domestic activities.