Featured in the EXARC Journal
Experimental Archaeology
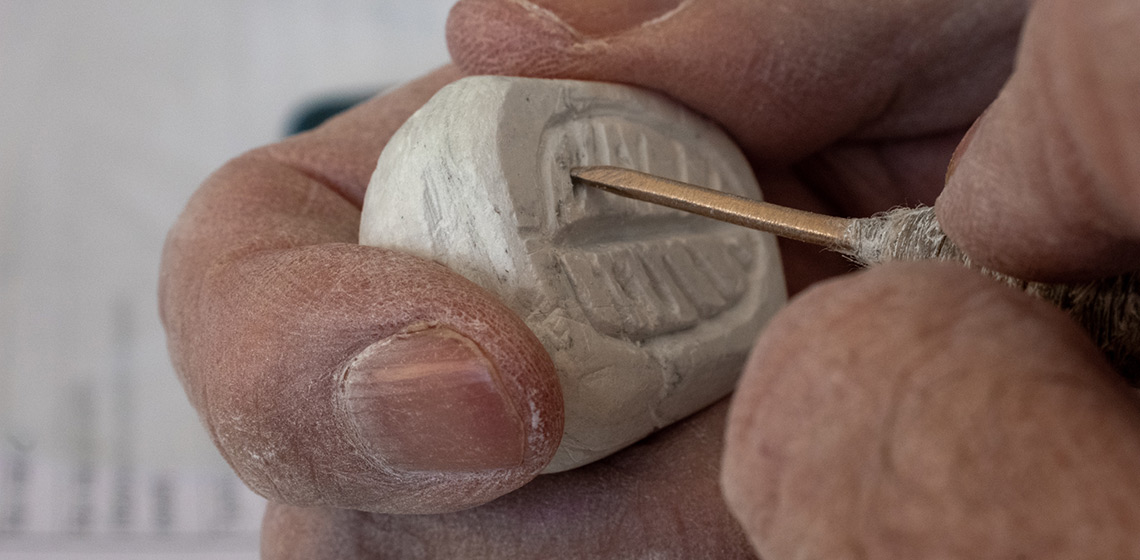
Leave your Stamp: Reconstruction of the Scarab Production Chain
Introduction
Scarabs were the most common type of seal-amulet in Egypt and the southern Levant during the second millennium BC, spanning the Levantine Middle and Late Bronze Ages (Keel, 2004, pp.73–101; Ben-Tor, 2007, p.119).
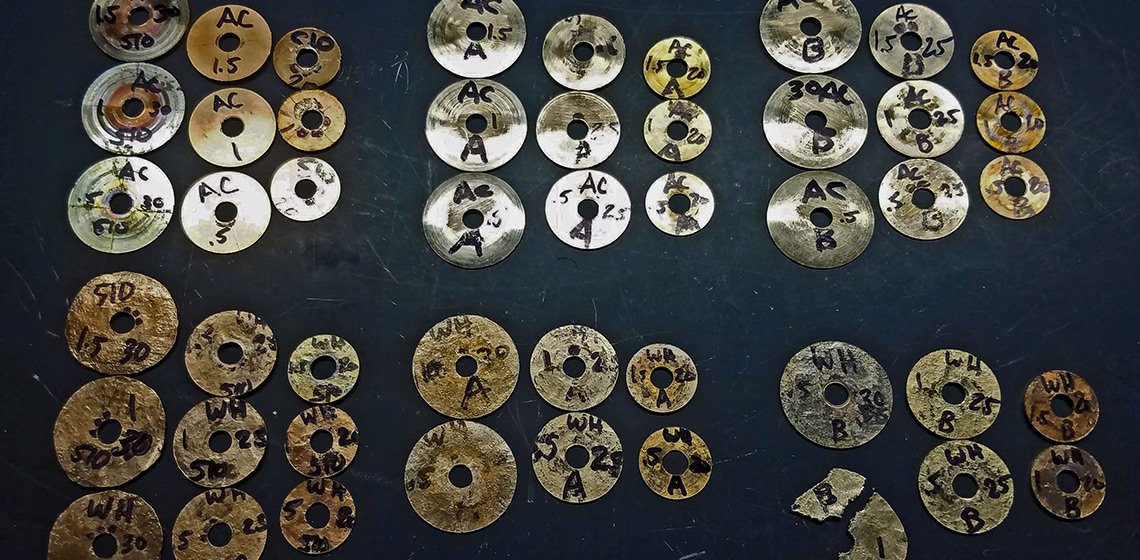
An Experimental Approach to Ancient Egyptian Metalworking: The Mysteries of the Sesheshet
Introduction
In our research, we investigated the metallic properties ancient Egyptian copper-alloy loop sistra that first appear during that first half of the 12th Dynasty (ca.